Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
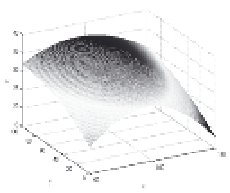
Surface 1 (S1)
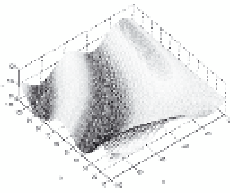
Surface 2 (S2)
Surface 3 (S3)
Mathematic
al surfaces
Randomly
sample
points
Table 2. Mathematical surfaces and distribution of randomly sample points
3.2 Design of evaluation indices
The interpolation result can be regarded as an original surface recovered by sample points.
It has two implications, i.e. one is to reflect the closeness between the original surface and
the recovered one on the value, and the other one is to recover the structural features of the
original surface. It means that the interpolated surface should as far as possible keep the
characteristics of the original surface both on statistics and structures, which should be
considered for the accuracy assessment of the interpolation results as well.
The evaluation indices about statistical features mainly include RMSE (Root Mean Square
Error), ME (Mean Error) and spatial autocorrelation. In this study, RMSE and ME are
selected to describe the quality of the interpolation functions. For following the first law of
geography (Tobler, 1970), the original surface itself has a strong spatial autocorrelation, so as
to the whole interpolated surface. As a result, the surface acquired by interpolations should
keep the spatial autocorrelation measured by Moran'I here, or else leading to a meaningless
result with an almost randomly interpolated surface. What's more, another two spatial
indices, volume and surface area are chosen to reflect the maintenance of overall
performance after interpolation. The volume stands for the room above a datum plane and
under an original surface or an interpolated surface whose area is measured by surface area.
Structural characteristic is the other important evaluation method. It can be regarded as the
skeleton of a surface, determining its geometric shape and basic trend, on which the
interpolated surface should be in accord with the original one. For the integrity of the
structural characteristic, so far there is lack of a suitable quantitative index. In this study, a
method of contour-matching has been applied to compare and analyze different
interpolations qualitatively, by means of overlaying the contours generated from an
interpolated surface and the original one. If these overlaid contours match generally without
great deviation or distortion, it can be induced that the structural characteristic of the
surface has been kept well after being interpolated, or the structural characteristic will be
lost leading to a fault result.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search