Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Soil types % of area HSG
Latosol 2.3 A
Podzolic 17.7 B
Inceptisol 56.3 C
Organic 23.7 D
Table 2. Soil types, % area in the watershed and their respective Hydrologic Soil Group
(HGS) according to Lombardi- Neto et al. (1991) and Embrapa (1999)
5.3 Fuzzy SCSCN model
For the developed model, each input variable was coded, fuzzified and, subsequently, input
into the fuzzy inference system for decision making, using the PCRaster EML (Wesseling et
al., 1996). The implementation of the computer model followed three steps: (i) the soil and
cover maps were transformed in a fuzzy set using the membership functions (linear and
bell-shaped); (ii) using the fuzzy inference system, the CN map was generated based in the
fuzzy soil map and the fuzzy cover map (both developed in the previous steps); (iii) runoff
calculation.
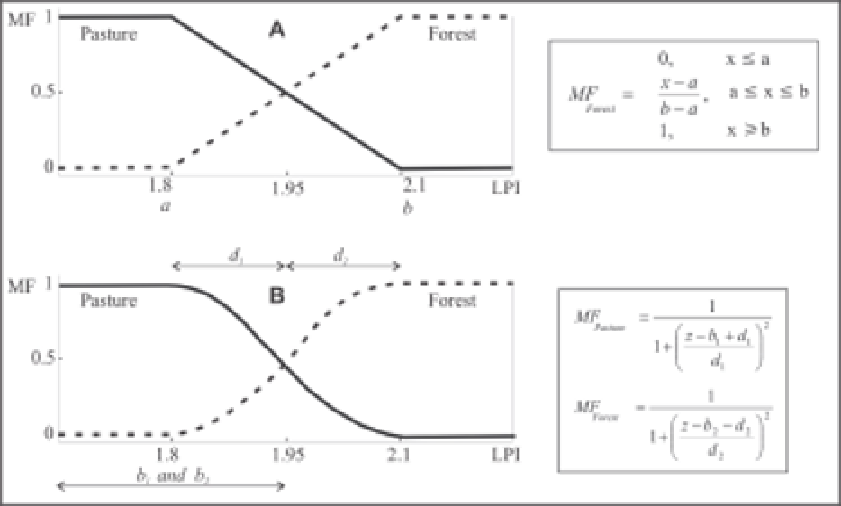
5.3.1 Fuzzy soil map
Using the methods of fuzzy logic on polygon boundaries makes it simple to incorporate
information about the nature of the boundaries. In this paper, the map-unit approach
described for Burrough and McDonnell (1998) was employed. This approach assumes that
the width of the transition zone is the same in all map boundaries. Information about the
type of boundary was converted to parameters for two fuzzy membership functions (linear
and bell-shaped) (Fig. 4), which were applied to the distance from the drawn boundary.
Fig. 4. Membership functions: (A) linear; (B) bell-shaped





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search