Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
The volcanism is divided into two periods: upper Jurassic-lower Cretaceous, a period
corresponding to a phase of extension of the Arabian plate margin, it corresponds to the
Bhannes-Tayasir area of Syria sequence, constitutes isolated lavas or covered by the
Neogene eruption, especially in the south of the country (west of Damascus), and in the
center (Nabi Mata region) (Dubertret 1962,Ponikarov 1967,Laws and Wilson 1997).More
recent Neogene-Quaternary eruptions are related to the formation of the Red Sea (24-16Ma),
and Dead Sea rifts (8-0,4 Ma) (Ponikarov 1967, Bohanon et al.1989,Camp et Roobol
1989,Baker et al 1997,Chorowicz et al 2005). A number of eruptions have been identified
from 17 Ma to present. The last volcanic eruption took place in the South of the country,
about 10000 years ago, as the end of the last eruption (<1Ma) (Dubertret 1933, Baker et al
1997).
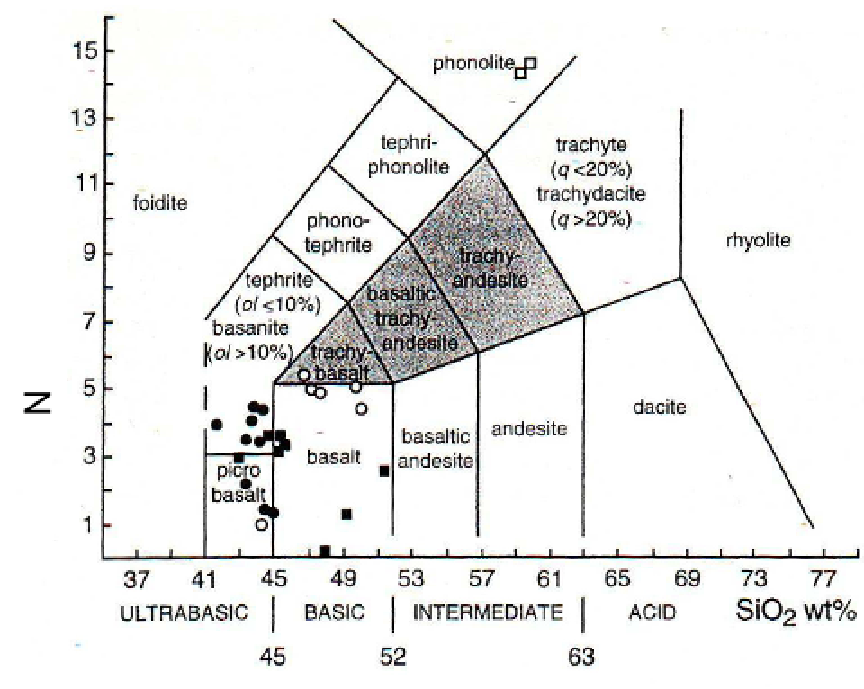
Erupted lavas are in general very basic.rock compositions , cover the basalt-, picrobasalt-,
and basanites fields on the diagram of Le Bas et al.(1986), (Fig.4),corresponding to a low
differentiated magma(Ismail et al.2008). Major and trace elements data show overall
similarities between recent and ancient ones, with however a more distinct alkaline trend
and stronger variations of LILE-elements for recent lavas. These data involve small volume
melt fractions.
Fig. 4. Total alkalis-silica diagram of Le Bas et al (1986) for the basaltic rocks along the Syrian
rift (Bilal and Touret 2001).









Search WWH ::

Custom Search