Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
4.
Seismic wavelet extraction and initial model creation
Establishing a reasonable initial geological model is the key for getting a good pseudo-
acoustic seismic inversion. In fact it is a process of deciphering interpolation and
extrapolation of well data under the constraints of the geological concept; the quality of the
seismic inversion results are largely dependant on the initial model, which is decided by
previous geological knowledge. In order to acquire a good model of impedance inversion,
we not only replace the sonic logging curve (ac) by the GS logging curve and by extract
Ricker wavelet from the target layer, but also combine the available well information based
on the synthetic seismograms calibration and test runs repeatedly.
5.
Pseudo-acoustic 3D seismic inversion
On the Strata5.2 inversion software platform, the GS, the GS pseudo-acoustic 3D seismic
inversion data are obtained by calculation after importing the GS. The results show that 3D
seismic inversion data based on gr+sp logs reconstruction is better than the conventional 3D
seismic inversion using ac+den loggings to distinguish the internal structure of the
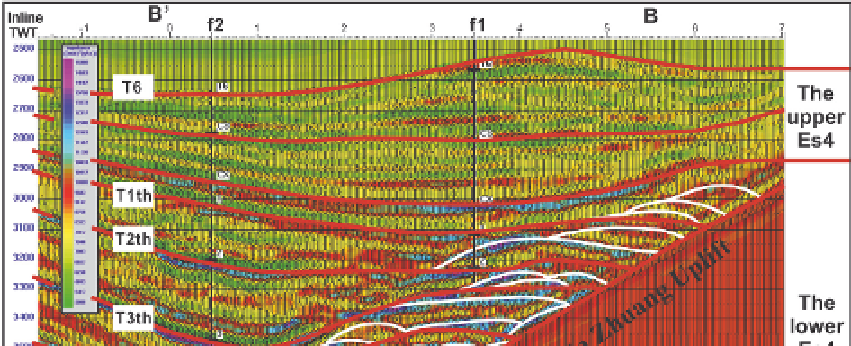
nearshore subagueous fans (Figs. 5, 6)
Fig. 6. 3D seismic reflection characteristics of the internal structure in the nearshore subaqueous
fans based on GS 3D seismic inversion data along line B'B (see Line L location in Fig.1)
4. 3D seismic sedimentology analysis of nearshore subaqueous fans
4.1 Evolution characteristics of seismic palaeogeomorphology of nearshore
subaqueous fans
By using the GS pseudo-acoustic 3D seismic inversion data coupled with calibration of the
synthetic seismograms, the internal sub-facies in each member of the lower Es4 Formation
can be identified and the temporospatial evolution of the nearshore subaqueous fans can be
extrapolated (Fig.6). The analysis finds that each member of the lower Es4 generally consists






Search WWH ::

Custom Search