Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
5. Impact of the pre-processings on the fractal properties of the airborne
gamma ray measurements
Once all the corrections are applied, the corrected measurements grid is regrided using two-
dimensional interpolation algorithms to get a regular sampled grid which is processed by a
local regularity analysis.
The set of operations (corrections and interpolations) affects the stochastic component of the
raw airborne spectrometric measurements, which holds information about heterogeneities.
Therefore the fractal properties of the raw data may be changed.
In the first stage, we have obtained the ''corrected'' and the ''corrected and interpolated''
data grids from the ''raw'' grid data corresponding to the measurements of the three
channels: K, Th and U. The 2D-interpolation algorithms used in this study are: the triangle-
based linear, the triangle-based cubic and the nearest neighbor interpolation algorithms.
Since the results obtained by the different interpolation methods are close, only those related
to the triangle-based linear algorithm are presented.
First, five vertical profiles are extracted from the three considered grids (''raw'', ''corrected''
and ''corrected and interpolated '' grids) from the measurements of the three channels
(Fig.2). The Fourier amplitude spectrum and the local Hölder exponent
H
(
x
) are computed
for each data profile.
Major accident
Suture zone
Palaeozoic cover
(1)
western branch (pharusian chain)
2
3
4
5
1
(2)
central branch (pharusian chain)
(3)
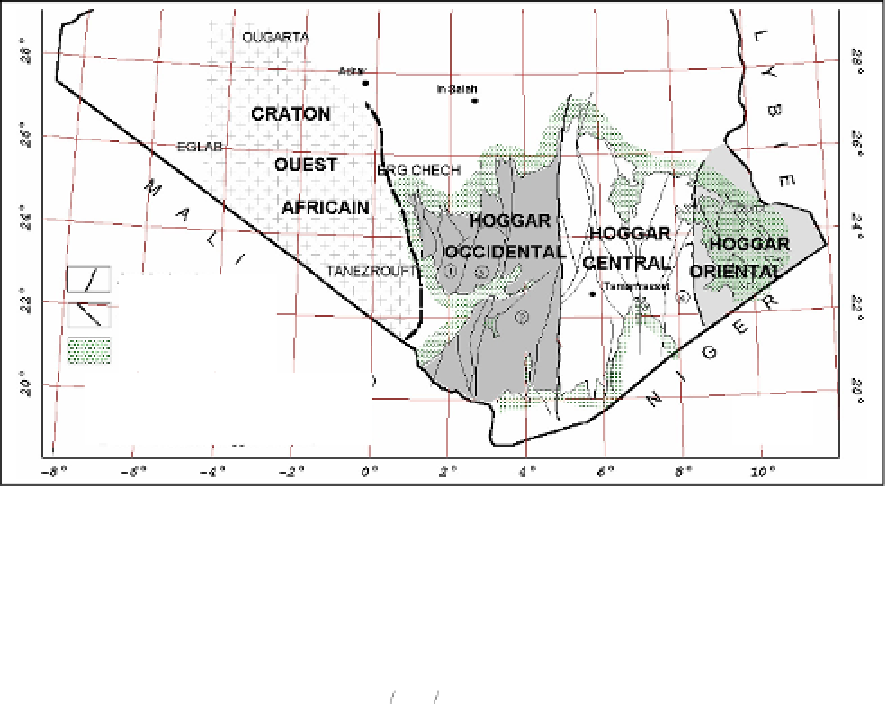
In-ouzzal mole (Western Hoggar)
Profile
(4)
Issalane mole (Eastern Hoggar)
Fig. 2. Position of the five profiles extracted from the GR measurements (in red).
(The geological map of the Hoggar, from Caby
et al.
, 1981).
Regarding the computation of
H
(
x
), we need a sequence
S
k,n
(
i
) defined by the local growth of
the increment process:
m
Si
Xj
1
X
j
,
1<k<n
(4)
k,n
n
1
jik ik
2
2








Search WWH ::

Custom Search