Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
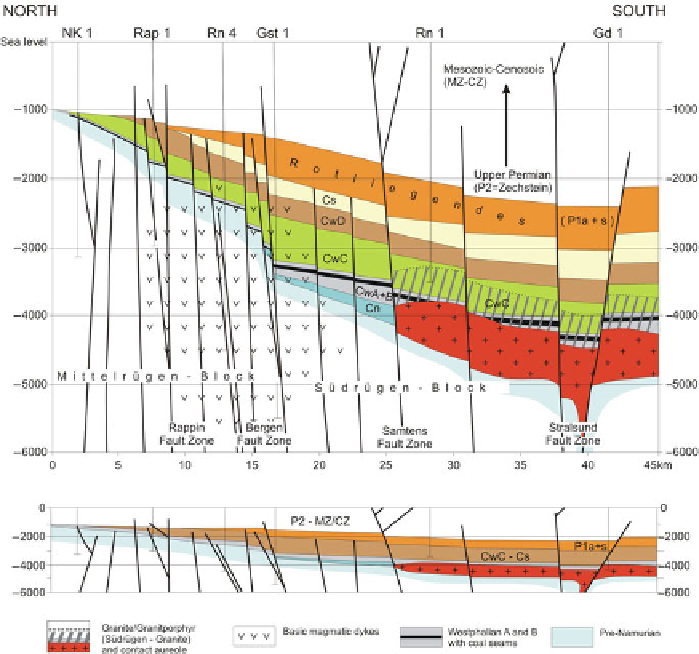
Baltic basin. The subsidence history from the Permian to the Mesozoic is described
2.3 Basin Subsidence and Geodynamic Evolution
The continental crust of the Baltic region formed during the Palaeoproterozoic
granites and associated igneous rocks during the time period between 1.67 and
Volcanic and sedimentary rocks mainly filling graben structures are spatially
associated with Mesoproterozoic intrusions. The largest feature of this type of
extensional depressions is the Bothnian Sea depression. It has many characteris-
tic features of a palaeo-rift such as a topographic low, a thin crust, large crustal
Bothnian aborted rift is probably a part of a honeycomb-like wide rift area that