Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
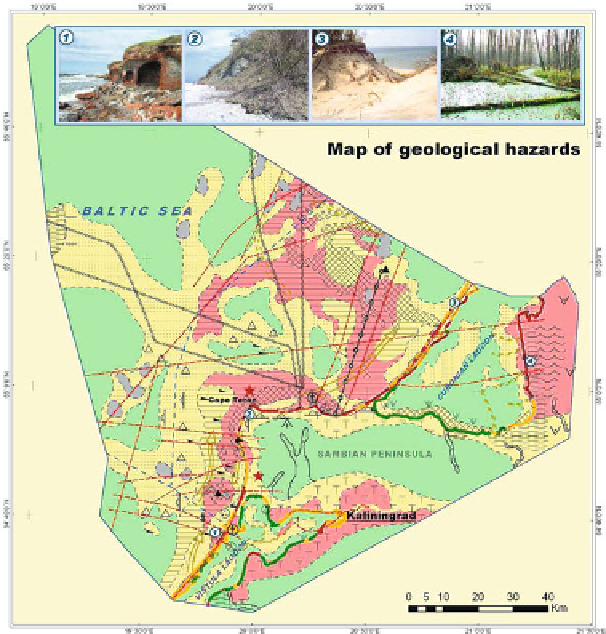
Fig. 16.3
Map of geological hazard potentials of the southeastern Baltic and its coastal zone
within Kaliningrad region (legend on Fig.
16.2
)
. Pictures:
1,
destruction of fortress (the Vistula
Spit);
2,
landslide (the Sambian Peninsula) (photos by D. Ryabchuk);
3,
dune blowup (the Curonian
Spit, photo by V. Boldyrev);
4,
swamping (the Neman Lowland, photo by I. Lysansky)
16.4.2 Exogenic Processes
At present, the
exogenic processes
can be considered as much more important and
harmful for the Baltic Sea region due to their wide extension and activity. Among
them,
coastal erosion
, caused mainly by storm surges, is one of the most intense and
hazardous processes.
16.4.2.1 Coastal Erosion
Erosional processes are extremely active along the open Baltic Sea coast of the
Kaliningrad area. The average rate of the cliff retreat of the Sambian Peninsula
shoreline recession is 0.5-0.7 m/year. During storm surge (usually one in 5-7 years),