Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
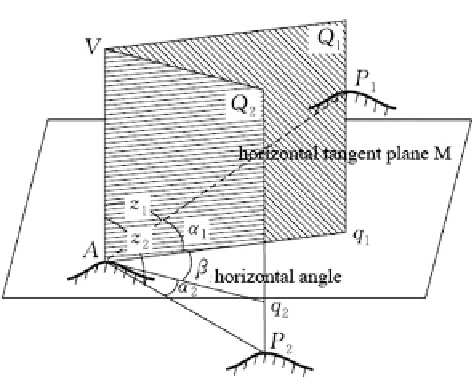
Fig. 2.1 Horizontal and
vertical angles
angle to P
1
and P
2
from A. The horizontal angle is measured clockwise in the
horizontal plane from 0
to 360
.
Vertical Angle
The angle between the line of sight AP
1
and its horizontal Aq
1
is called the vertical
angle to the sighted point P
1
from A, denoted by
ʱ
1
. Likewise, the angle between the
line of sight AP
2
and its horizontal line Aq
2
is referred to as the vertical angle to the
sighted point P
2
from A. Therefore, a vertical angle is the angle between the line of
sight, which is the collimation axis of the telescope, and its corresponding horizon-
tal, which includes the angle of elevation and angle of depression.
A vertical angle is measured in the vertical plane from 0
to
90
, positive
above the horizontal (see Fig.
2.1
,
ʱ
2
).
The angles Z
1
and Z
2
between the plumb line AV and the lines of sight AP
1
and
AP
2
are called the zenith distances from point A to the sighted points P
1
and P
2
.
As illustrated in Fig.
2.1
, the sum of the vertical angle and the zenith distance of
a target is 90
, namely
ʱ
1
) and negative below (see Fig.
2.1
,
90
:
ʱ þ
Z
¼
ð
2
:
1
Þ
According to this relation, the vertical angle and the zenith distance can easily be
converted one to the other.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search