Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
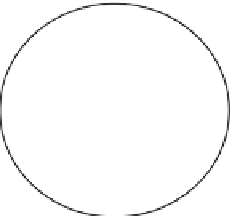
Fig. 1.1 Determination of
the Earth's radius
B
S
γ
A
O
R
other measuring instruments greatly improved the accuracy and laid technical
foundations for the development of geodesy. So, we can claim that geodesy was
established in the late seventeenth century.
Development of Arc Measurement
From 1683 to 1718, G.D. Cassini and J. Cassini from France measured the arc
length of a 8
20
0
arc of the meridian across Paris by triangulation and deduced the
semimajor axis and the flattening of the Earth ellipsoid from the lengths of its two
arcs and the astronomical latitude measured at the two endpoints of each arc. Since
the observation of the astronomical latitude did not reach the required accuracy and
the two arcs were similar, they obtained a negative value for the Earth's flattening;
namely, that the Earth is an ellipsoid elongated at the poles, which was the opposite
of the deduction by Huygens based on the laws of mechanics. To clarify this doubt,
in 1735 the French Academy of Sciences sent two survey teams to Lapland
(situated on the border of Sweden and Finland) with a high latitude and Peru near
the equator for meridional arc measurements. Their work finished in 1744 and the
survey results from these two places certified that the higher the latitude, the longer
the meridional arc per degree; namely, that the Earth is an ellipsoid flattened at the
poles. Since that time, the physical assertion of the shape of the Earth is strongly
supported by the results of arc measurement.
Another famous arc measurement was made by J.B.J. Delambre from 1792 to
1798, during which he measured the new meridional arc of 9
40
0
in France. From
the data of this new arc and the meridional arc measured in Peru from 1735 to 1744,
he deduced the length of a quadrant of the meridian and took one ten-millionth of it
as the length unit named as one meter (1 m); this was the origin of metric system.
From the eighteenth century, to meet the needs of precise mapping, some other
European countries started arc measurement and developed the layout method from
along the meridional direction to the crisscrossed triangulation chains or triangula-
tion networks. This work is no longer called arc measurement but astro-geodetic
surveying.
In order to draw the Complete Atlas of the Empire (Huangyu Quantu), a large-
scale astro-geodetic survey was conducted during Kangxi's reign in China's Qing
Dynasty (1708-1718). The survey also proved that the meridional arc per degree at


Search WWH ::

Custom Search