Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
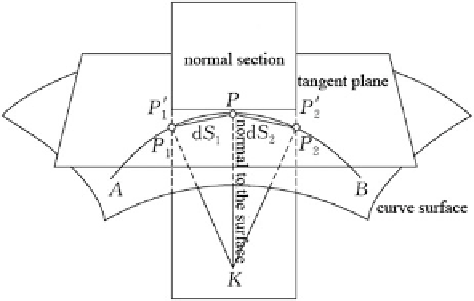
Fig. 5.21 Definition of
geodesic (two sides of the
two triangles in the middle
of the figure, left-side dS
1
and right-side dS
2
)
shortest route between two points. However, the projection of the arc element of
other curves like the arc element of an oblique curve onto the tangent plane will be a
curve element without fail. The parallel is an oblique curve. In Fig.
5.22
,
PP
1
andPP
2
are the two adjacent arc elements of point P on the parallel. Its
orthographic projection onto the tangent plane T at point P is the curve element
P
0
1
PP
0
2
.
The Geodesic Is the Connection of the Arc Elements of Numerous Normal
Sections
The adjacent two arc elements of a point on the geodesic are on the same normal
section plane, and hence they can be considered the arc elements of two normal
sections with their orientations 180
apart at this point. Therefore, the geodesic is
the connection of the arc elements of these normal sections at each point. If we draw
a straight-line traverse on the ellipsoid, as shown in Fig.
5.23
, and let the deflection
angle be 180
, then the sides are so short that the normal section and reverse normal
section
coi
ncide with each other. As shown in Fig.
5.23
, ab and ba coincide and
become ab. This short-side straight-line traverse is the geodesic.
The normal sections on the ellipsoid are not geodesics except for the meridian
and equator. Note that the normal section is a curve lying in a plane that contains the
normal at one point and passes through the other point, whereas the geodesic is any
normal section that passes through every point along the curve.
The Geodesic Is a Curve of Double Curvature on the Surface of the Ellipsoid
Geodesics are on the surface of the ellipsoid. The bending of the ellipsoid causes the
longitudinal bending of geodesics, which is represented by the curvature at each
point. Since each point along the geodesic has a different longitude and latitude, the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search