Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
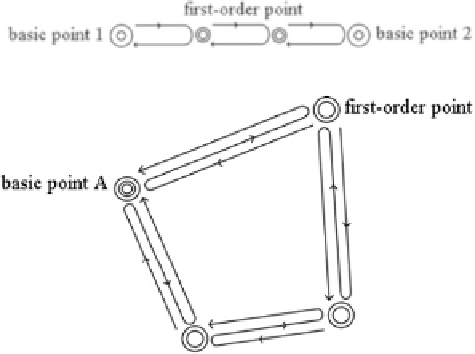
Fig. 3.28 Connecting line
of gravity measurement
Fig. 3.29 Closed loop of
gravity measurement
and terminating (closing) either at a second basic point, forming a connecting line
(see Fig.
3.28
), or at the same starting point, forming a closed loop (Fig.
3.29
).
The point spacing of the first-order gravity network is approximately 300 km
along the primary traffic routes. The number of line segments of the closed loop
must not exceed five. The mean square error of the gravity difference between the
line segments connected to each other must not exceed
10
8
m/s
2
. The first-
order gravity points are required to be determined by LCR-G gravity meters or
other precise gravimeters of equivalent quality. The constants and parameters of the
instruments must be calibrated between the national basic gravity points or at the
national-level stations for gravimeter calibration.
The second-order gravity point is a further extension of the basic network and
the first-order gravity network. Its primary goal is to provide effective control for
densifying gravity measurement. Hence, the establishment technique and density of
the second-order gravity point can be determined according to the need for densi-
fying gravity measurement. It is required that the higher-order gravity points and
their derived points be used as initial points, established in the form of a closed loop
or a connecting line. The line segments must generally not exceed five, but in harsh
areas the number can reach eight. It is also acceptable to start from first-order
gravity points and higher to develop second-order points in spur lines of one or two
segments.
Gravity points in the densification network are established according to the
different needs and complexity of the gravity field of the surveying area. The
densification points are characterized by great density, small point-spacing, and
fairly low-level accuracy. Therefore, gravimeters of any models installed at present
can be adopted. The requirements can be readily satisfied using two instruments
carried by automobiles to observe a survey line.
Determining the coordinates and heights of gravity points is an essential part of
relative gravity measurements because the accuracy of coordinates and heights will
directly affect the accuracy of gravity anomalies at gravity points. The mean square
25
Search WWH ::

Custom Search