Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
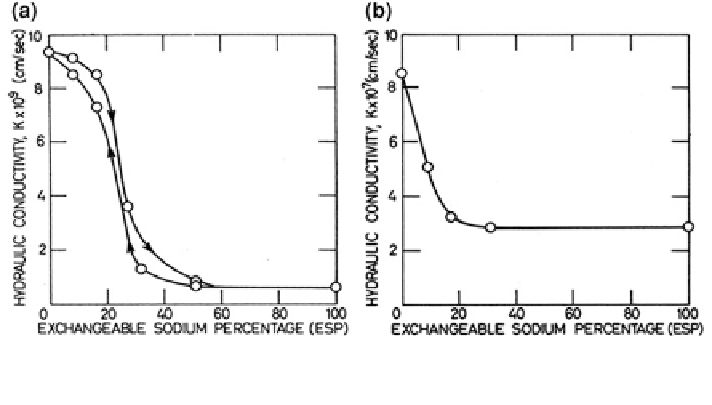
Fig. 18.24 The hydraulic conductivity of a the clay membrane, and b clay pastes, as a function
of exchangeable sodium percentage, ESP (modified after Yaron and Shainberg
1973
)
mineralogy. McNeal and Coleman (
1966
) indicated that in soils where the clay
minerals are dominated by the extent of 2:1 layer silicates, and where there are
moderate amounts of montmorillonite, ESP values in excess of 15 can often be
maintained without causing a serious reduction in HC, provided that the concen-
tration of the permeating solution is about 3 meq/L. Yaron and Thomas (
1968
)
studied the effect of ESP on the hydraulic conductivity of various Texas soils,
finding that a 20 % HC decrease was produced by an ESP of 10 in montmorillonite
soils, by an ESP of 16 in a soil with mixed mineralogy, and by an ESP of 23 in a
kaolinite soil.
The composition of the permeating water—in terms of the ratio between
sodium and other cations—has a significant effect on the exchange process and on
the hydraulic conductivity of soils. In dealing with the effect of saline or waste
water on HC, one must consider the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR). Under
dynamic conditions, when an initially nonsodic soil is irrigated with sodic water,
the HC decreases continuously until the exchangeable sodium in the entire soil
profile equilibrates with the permeating solution. Yaron and Thomas (
1968
)
showed that this decrease in HC is characterized by a curve whose shape depends
on the nature of the soil, the cationic composition, and the total salt concentration
of the permeating solution. The hydraulic conductivity depends on the mean ESP
of the soil profile and is independent of the volume of the effluent. Moreover, an
increase in SAR results in a decrease in hydraulic conductivity. Figure
18.25
shows the reduction in HC when three electrolyte water solutions with one value of
total concentration (11 meq/L) and three SAR values (7.5, 14.0, 28.0) were passed
through columns of a Burleson loamy clay vertisol. At equilibrium, an SAR value
of 7.5 resulted in a 15 % decrease in HC, whereas an SAR of 28 reduced initial HC
by 84 %. These results are in agreement with those of other parallel studies (e.g.,
Reeve
and
Tamaddoni
1965
;
McNeal
and
Coleman
1966
;
McNeal
1968
;