Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
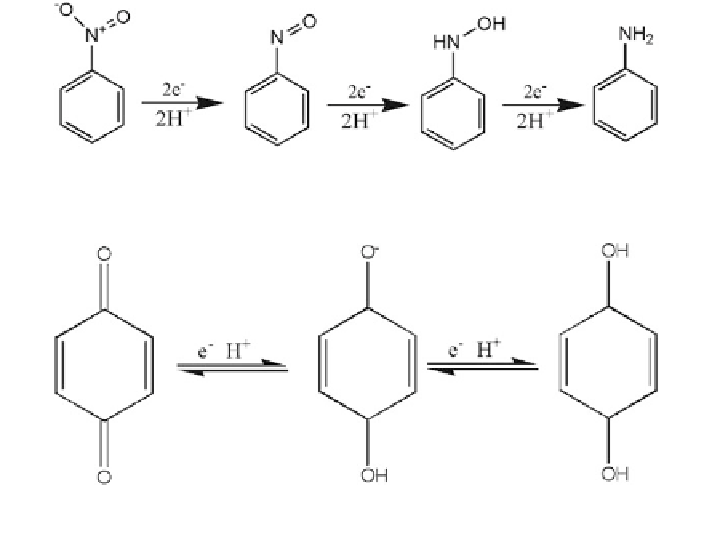
Fig. 13.1
Reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline
Fig. 13.2 Reduction of quinone to semiquinone and hydroquinone through two one-electron
transfer steps (Larson and Weber
1994
)
N-nitosoamine Reduction The reduction of N-nitrosoamines can occur across
either the N-N bond or the N-O bond. Both reactions ultimately result in the
formation of the parent amine and ammonia.
Quinone Reduction This is a reversible, one-electron transfer reaction to the
semiquinone radical, followed by a second, reversible electron transfer that results
in the formation of hydroquinone, as shown in Fig.
13.2
.
Reductive Dealkylation Reductive dealkylation involves replacement of an
alkyl group on a heteroatom by hydrogen. The reaction is considered to be mainly
biologically mediated and usually is important in the subsurface for transformation
of agrochemicals.
Photolysis Abiotic oxidation occurring in surface water is often light mediated.
Both direct oxidative photolysis and indirect light-induced oxidation via a pho-
tolytic mechanism may introduce reactive species able to enhance the redox
process in the system. These species include singlet molecular O
2
, hydroxyl-free
radicals, super oxide radical anions, and hydrogen peroxide. In addition to the
photolytic pathway, induced oxidation may include direct oxidation by ozone
(Spencer et al.
1980
) autooxidation enhanced by metals (Stone and Morgan
1987
)
and peroxides (Mill et al.
1980
).
Photolysis is an environmental process in which a substrate in a natural aqueous
solution is subjected to ultraviolet (UV) or visible light, causing its transformation.
Sunlight at the surface of the earth consists of direct and scattered light entering a