Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
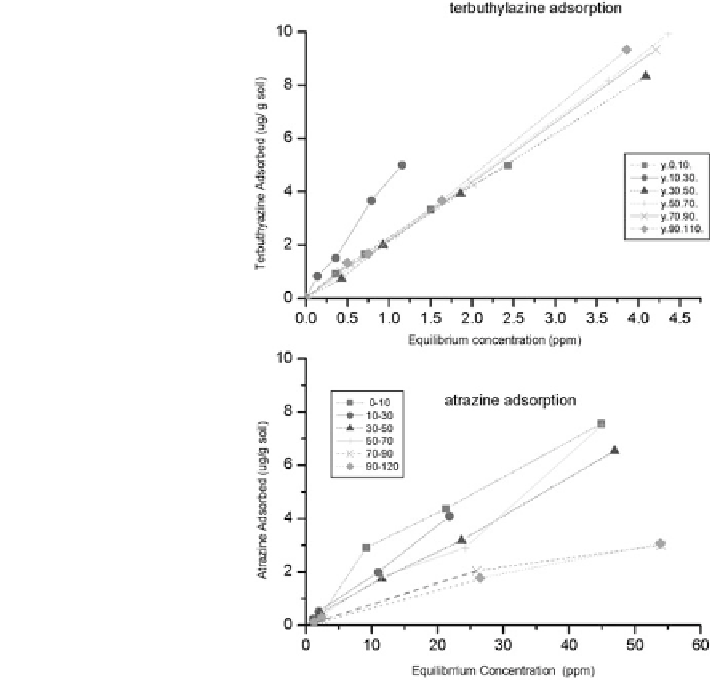
Fig. 8.32 Adsorption
isotherms of terbuthylazine
and atrazine at different
depths along the soil profile,
as affected by the vertical
variability of soil properties
(Dror et al.
1999
)
soil profile, following surface application and subsequent leaching by irrigation or
rainfall. Figure
8.32
shows adsorption isotherms of these two herbicides as
affected by the vertical variability of the soils. The adsorption isotherms are linear
along the soil profile. The K
d
coefficients of atrazine range from 0.10 to 0.21 mL/g,
while those of terbuthylazine range from 1.9 to 2.9 mL/g. The vertical variability
of K
d
, quantified in terms of the mean and standard deviation (SD), is K
d
= 0.15
with an SD of 0.04 for atrazine and K
d
= 2.17 with an SD of 0.36 for terbu-
thylazine. The effect of soil OM on herbicide adsorption is given by the distri-
bution coefficient on OC, K
oc
, obtained from the relation K
oc
= K
d
/OC 9 100,
assuming that OC = OM/1.7. The vertical spatial variability of K
oc
is similar to
those of K
d
.
Organophosphorus pesticides are used as an example of the adsorption of
nonpolar (nonionic) or slightly polar toxic chemicals. The phosphoric acid ester
group has a general formula (RO)
2
PO(OX), where R is an alkyl group and X is a
leaving group (see
Sect. 4.1.2
)
. In contact with clay surfaces or other earth
materials, such organic nonpolar molecules are retained on the surface. These