Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
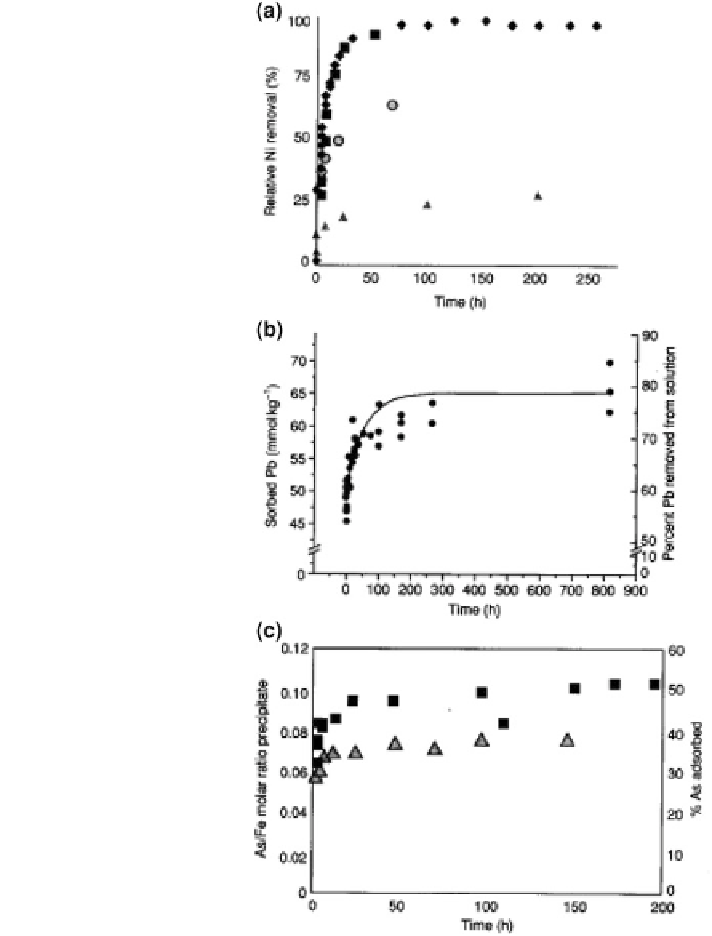
Fig. 8.27 Kinetics of metal
and oxyanions on soil
minerals and soil. a Kinetics
of Ni sorption (%) on
pyrophylite (black diamond),
kaolinite (black square),
gibbsite (black up-pointing
triangle), and
montmorillonite (open circle)
from a 3 mmol
-1
Ni solution,
an ionic strength
I = 0.1 mol
-1
NaNO
3
and a
pH of 7.5; b kinetics of
sorption on a Matapeake soil
from a 12.25 mmol
-1
Pb
solution, an ionic strength
I = 0.05 mol
-1
and a pH of
5.5; c kinetics of As(v)
sorption on ferrihydrite at pH
8.0 and 9.0. As(v) total
1 9 10
-4
mol
-1
; Fe (III)
total 5 9 10
-4
mol
-1
(black
square) adsorption at pH 8.0
(black up-pointing triangle)
adsorption at pH 9.0 (Sparks
2005
)
Sparks (
2005
) notes that in addition to diffusion processes, the formation of
metal hydroxide surface precipitates on phyllosilicates, metal oxides, and soils,
together with residence time effects, can greatly affect the release of heavy metal
and the hysteresis pattern. Aging of the metal hydroxide surface precipitate affects
metal release, enhancing metal stability on soil minerals. With time, heavy metal
sorption on soil minerals may develop a chain of processes leading to soil