Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
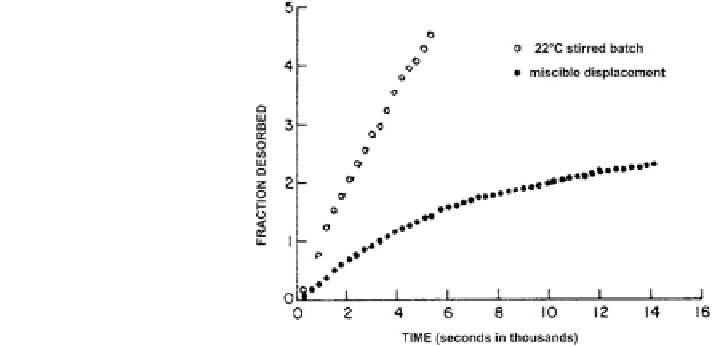
Fig. 5.10 Effect of
measurement technique on
sulfate desorption from soils
(modified after Hodges and
Johnson
1987
)
Johnson (
1987
) used two experimental techniques (rapidly stirred batch and
miscible displacement with slow flow rate) to study sulfate desorption and found
that, in the stirred batch experiments, the desorption readings were less than those
obtained by the miscible displacement technique (Fig.
5.10
). Even within the
miscible displacement technique, the time of leaching was found to have a major
effect. The estimated (by extrapolation) time required for complete desorption was
10-20 times greater than for adsorption.
Bowman and Sans (
1985
) compared two methods (dilution and consecutive
desorption) for measuring the desorption of selected synthetic organic pesticides
from organo-clay systems. Note that dilution of suspensions may increase the
accessibility of an adsorbing surface, so this method is not strictly comparable with
the classical method. In all cases studied, only minimal hysteresis in the desorption
isotherm was obtained using the dilution method, whereas almost all systems
investigated with the consecutive desorption method exhibited considerably larger
hysteresis. Rao and Davidson (
1980
) also suggested that, in the case of pesticides,
the centrifugation-resuspension step is in some way responsible for the hysteresis
effect, explained by the fact that partially irreversible compaction of the adsorbent
during centrifugation greatly increases the time required for desorption.
5.8.3 Bound Residues
The term bound residue was adopted by the International Union of Pure and
Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in 1984. According to this definition and that of the
European Commission (adopted in 1991), nonextractable residues in soil are
chemical species, originating from pesticides, which are not extracted by methods
that do not significantly change the chemical nature of the residue. Fuhr et al.
(
1998
) expanded the meaning of bound residues to the ''compounds in soil, plant