Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
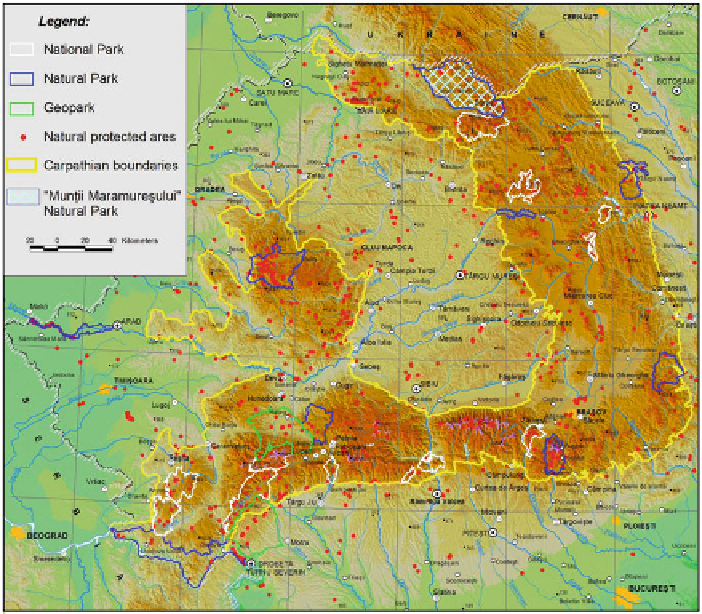
Fig. 21.1
Natural protected areas in the Romanian Carpathians
Over the last 20 years, Romania has experienced radical changes, mainly
related to global environmental change and to regional and local socio-economic
transformations. After the fall of the communist period, mountain areas are facing
new landscape-related problems in terms of climate change, biodiversity loss,
trans-boundary pollution, trade in endangered species and waste management
(Balteanu et al.,
2008
). In order to protect the natural environment in the Romanian
Carpathians, 22 major protected areas totalising approximately 1 million hectares,
among which 12 national parks, 8 natural parks and 2 geoparks, as well as some
600 reserves and natural monuments totalling 50,000 ha, were declared (Fig.
21.1
)
(Balteanu et al.,
2009
).
Maramures Mountains are the highest mountain massifs built up on crystalline
schists and flysh folds rising up to approximate 2,000 m (Farcau Peak 1,957 m),
located on the northern boarder of Romania with Ukraine (Balteanu et al.,
2006
).
In 2005, Maramures Mountains were declared protected area, under the
Category
V IUCN - Protected Landscape-Natural Park
. Among the main characteristics for
this designation were: the original mountain landscape covered by forests alternat-
ing with alpine meadows, the presence of flora and fauna that is emblematic for
the Carpathians, developed within ecosystems which are still in balance (forests,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search