Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
as salicornia or saltwort, is a short, annual forb with
succulent leaves that grows on many salt flats and is
conspicuous when large numbers of the plant form a
scarlet band in late summer along the edge of white salt
deposits. Many salt flats are virtually unvegetated much
of the time. in the Laramie Basin, for example, mudflats
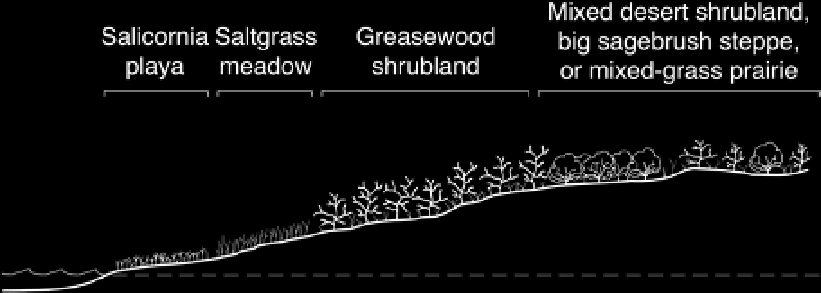
Fig. 5.6. Vegetation around desert playa wetlands changes
with distance from open water, probably because soil salinity
decreases and depth to water table increases. Salicornia, also
known as red swampfire, is a succulent that tolerates high
salinity.
hydrophytes (such as cattails and hardstem bulrush)
dominate the deeper water. Different plants and ani-
mals are associated with each of the zones, an illus-
tration of how patchy environments contribute to the
biological diversity of the landscape as a whole.
Most large marshes are found in areas that have
received water from irrigation or diversions. For ex-
ample, cattails occur along the shore of ocean Lake
in the Wind River Basin, which receives much of its
water supply from irrigation drains. in Goshen Hole
of eastern Wyoming, marshes with cattails and bul-
rushes occur on the edges of the lakes and ponds
enlarged or constructed on the table Mountain and
Springer / Bump-Sullivan Wildlife Habitat Manage-
ment units. in the Laramie Basin, the water levels of
Hutton Lake national Wildlife Refuge are managed by
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service biologists to maintain
large stands of hardstem bulrush.
Playa Wetlands
Wetland desiccation is more likely to occur at low eleva-
tions, which sometimes leads to the formation of playa
evaporates completely—more frequently in playa wet-
lands than in marshes—the salts precipitate and become
sufficiently concentrated to exclude most plants. only a
few halophytes tolerate such environments, including
greasewood, red swampfire, and saltgrass (see table 5.1
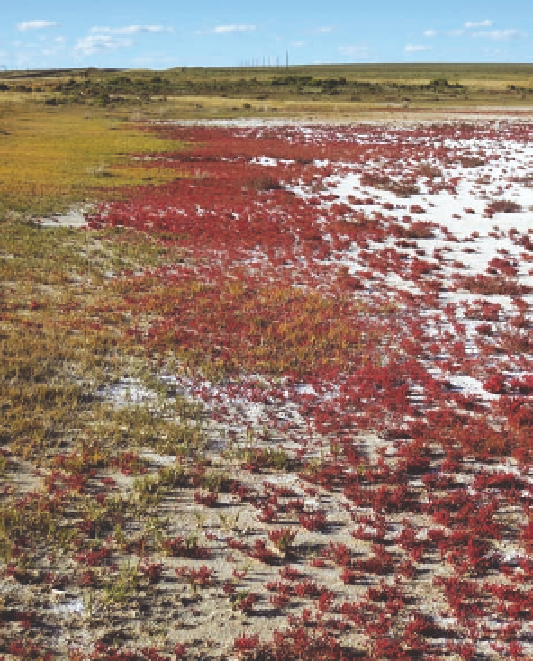
Fig. 5.7. Playa wetland in the fall, when most of the water is
evaporated and red swampfire is conspicuous on the white,
salt-crusted soil surface. the tan vegetation on the left is
dominated by saltgrass. Photo taken in the Laramie Basin at
an elevation of 7,000 feet.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search