Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Little Brooklyn Lake
10361 ft
3
Wet
wet
Early 20th Century
Wetness
:
48 in
Pre-1900: Multiple droughts >15 years
- many of greater severity than 1950s
2
1
0
-1
Late 20th Century:
Relatively wet &
no major droughts
-2
50+ year
megadroughts
Dry
dry
-3
900
1000
1100
1200
1300
1400
Year
1500
1600
1700
1800
1900
2000
Foxpark
9065 ft
16 in
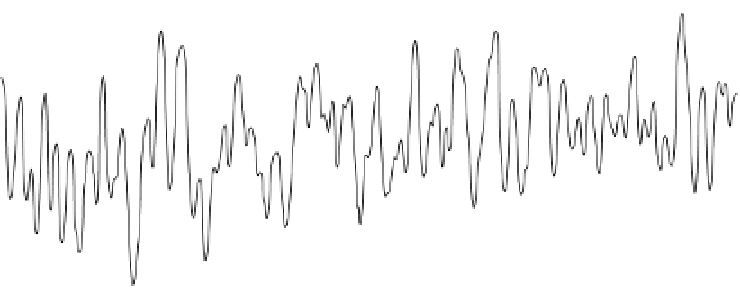
Fig. 3.5. (above) Drought history for the past 1,100 years in the Green River Basin of southwest
Wyoming, as reconstructed from tree rings. the graph shows estimated values for the Palmer
Drought Severity index, a measure of drought severity. Positive values of the index represent
relatively wet conditions; negative values indicate drought. each point on the graph repre-
sents the mean over a 25-year period. See also fig. 2.11. Based on data from cook et al. (2004);
adapted from Gray and Andersen (2009).
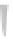
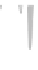
Fig. 3.6. (right) climate diagrams for southeastern Wyoming that illustrate climate change with
elevation. the graphs show mean monthly precipitation (top line) and mean monthly tempera-
tures from January to December. Black areas indicate periods of drought, when the precipitation
line drops below the temperature line. each unit on the vertical axis is 20 mm of precipitation
(water equivalent) or 10°c. the number at the top of each diagram on the left is elevation (feet);
on the right, mean annual precipitation (inches). A break in the horizontal bar in the summer
indicates the frost-free period; a black bar indicates that the mean daily minimum during a
month is below freezing, and a hatched bar indicates months when the lowest temperature is
below freezing. on the vertical axes, to convert millimeters of precipitation to inches and de-
grees centigrade to degrees Fahrenheit, see appendix A. Based on data from Martner (1986) and
the Wyoming Water Resources Data System at the University of Wyoming.
Laramie
7267 ft
10 in
Cheyenne
6125 ft
13 in
occurs most abundantly in the basins of the western
two-thirds of the state, where the proportion of snow
and summer rainfall occur in the eastern grasslands
(fig. 3.5), where big sagebrush often is restricted to
places where snowdrifts develop.
Periodic droughts characterize the mountains as well
as the lowlands, with those of the 1930s, 1950s, and
Much longer droughts have been identified using tree-
ring research in Wyoming's Bighorn Basin, with some
multidecadal droughts occur again? Understanding the
effects of drought on ecosystems and local economies
is a logical step toward developing a strategy for adapt-
ing to the droughts of the future. even today, water is a
limiting factor for economic growth.
mm
°C
0
J
D
MONTH


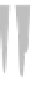










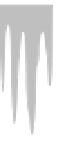









































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search