Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
are different for the Nazca plate and the Indo-
Australian plate. If these are indeed flow vec-
tors then fertile heterogeneities in the astheneo-
sphere will show little relative motion under a
given plate. In fact, the vectors are similar in rel-
ative motions to hotspot tracks, suggesting that
hotspots may have a shallow origin. The mantle
is likely to be heterogenous in its melting point
and ability to produce basalt (fertility). If
fer-
tile blobs
are embedded in the upper man-
tle return flow channel the above map will give
their relative directions and velocities. For exam-
ple, fertile blobs under the Pacific plate will trace
out parallel paths and move at about the same
velocity with respect to one another. The blobs
under the African and Antarctic plates will be
almost motionless. The blobs under the Indian
plate will move north and those under the Nazca
plate will move east-west. These are similar to
the motions of hotspot tracks and to the relative
motions of hotspots. If the return flow channel
is 3 to 4 times thicker than the plates, then the
velocities will be 3 to 4 times slower than plate
velocities. This is an explanation for the near fix-
ity of hotspots relative to one another.
VELOCITY
SURFACE
9.0
9.5
10.0
10.5
11.0
11.5 km
MgSiO
3
ILMENITE
/
s
Fig. 20.13
Variation of compressional velocity with
direction in the ilmenite form of MgSiO
3
. This is a stable
mineral below about 500 km in cold slabs. MgSiO
3
-ilmenite is
a platy mineral and may be oriented by stress, flow and
recrystallization in the slab. Ice (in glaciers) and calcite (in
marble) have similar crystal structures and are easily oriented
by flow, giving anisotropic properties to ice and marble
masses. The deep slab may also be anisotropic.
Shear-wave splitting and
slab anisotropy
MODE 0
T
10
In an anisotropic solid there are two shear
waves, having mutually orthogonal polariza-
tions, and they travel with different velocities.
This is known as
shear-wave splitting
or birefringence
. Since shear waves are
secondary arrivals and generally of long period,
it requires special studies to separate the two
polarizations from each other and from other
later
0.
VS
VSV
VSH
arrivals.
Deep-focus
events
are
the
most
suitable
for
this
purpose;
many
studies
have
clearly
demonstrated
the
existence
of
1.438
−
0
400
800
1200
1600
2000
splitting.
Ando
et al.
(1983), in an early pioneering study,
analyzed nearly vertically incident shear waves
from intermediate and deep-focus events beneath
the Japanese arc. The time delay between the
two nearly horizontal polarizations of the shear
waves was as much as 1 s. The polarization
of the maximum-velocity shear waves changed
Depth (km)
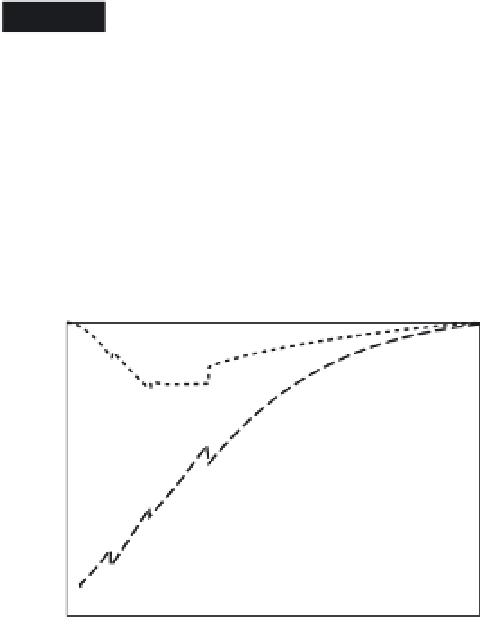
Fig. 20.14
Partial derivatives for a relative change in period
of toroidal mode (Love wave)
0
T
10
due to a change in shear
velocity as a function of depth. The solid line gives the
isotropic partial derivative. The dashed lines give the effect of
perturbations in two components of the velocity. Period is
720 s (after Anderson and Dziewonski, 1982).