Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
North
American
Plate
Eurasian Plate
Pacific
Plate
Caribbean
Plate
African
Plate
Cocos
Plate
Nazca
Plate
Indo-Australian
Plate
South
American
Plate
Antarctic Plate
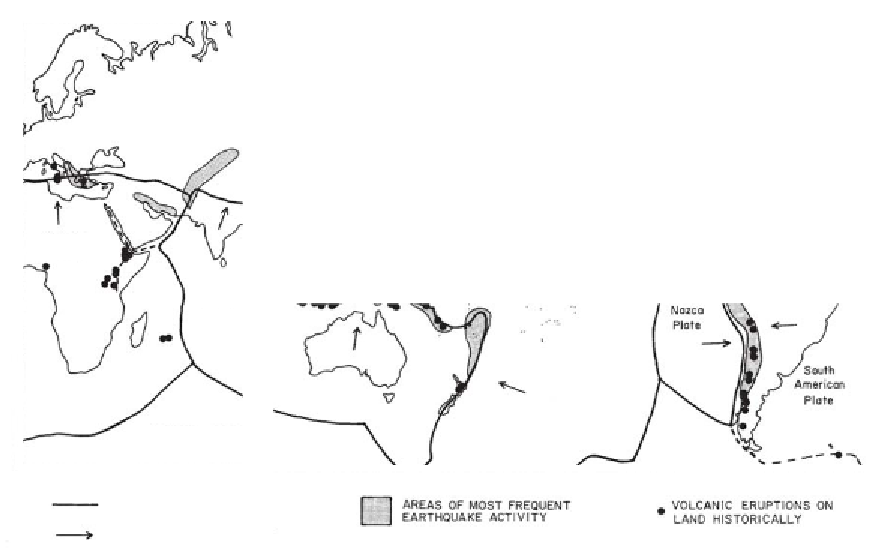
Plate boundary
Areas of most frequent
earthquake activity
Volcanic eruptions on
land historically
Direction of movement
Distribution of plate boundaries, intense earthquakes and historical land-based volcanic eruptions (based on Press & Siever, 1986; Bolt, 1993)
.
Fig. 9.1
The Mercalli scale of earthquake intensity.
Table 9.3
Maximum Acceleration
Corresponding
in mm s
2
Scale
Intensity
Description of effect
Richter Scale
I
Instrumental
detected only on seismographs
<10
II
Feeble
some people feel it
<25
III
Slight
felt by people resting; like a large truck
<50
<4.2
rumbling by.
IV
Moderate
felt by people walking; loose objects
<100
rattle on shelves.
V
Slightly Strong
sleepers awake; church bells ring.
<250
<4.8
VI
Strong
trees sway; suspended objects swing;
<500
<5.4
objects fall off shelves.
VII
Very Strong
mild alarm; walls crack; plaster falls.
<1000
<6.1
VIII
Destructive
moving cars uncontrollable;
<2500
chimneys fall and masonry fractures;
poorly constructed buildings damaged.
IX
Ruinous
some houses collapse; ground cracks;
<5000
<6.9
pipes break open.
X
Disastrous
ground cracks profusely;
<7500
<7.3
many buildings destroyed;
liquefaction and landslides widespread.
XI
Very Disastrous
most buildings and bridges collapse;
<9800
<8.1
roads, railways, pipes, and cables
destroyed; general triggering of other
hazards.
XII
Catastrophic
total destruction; trees driven from
>9800
>8.1
ground; ground rises and falls in waves.