Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
START
Calculate forcing:
Q
s
(1
-A
),
Q
u
,
∇
p
,
W
Momentum equation
∂
u
N
z
∂
v
....;
....
∂
t
∂
t
K
q
~ N
z
Heating and mixing:
∂
r
Turbulence:
K
z
...
∂
t
∂
E
T
∂
t
u, v
...
q
Ri
r
S
M
, S
H
N
z
, K
z
t
→
t
Δ
t
END
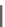
Figure 7.2
Simplified schematic of the links between the vertical velocity and density structure
required within the TCmodel during one time step to generate the eddy diffusivities and viscosities.
western Irish Sea. Comparison with observations in
Fig. 7.3b
shows that the model
generally does rather well in simulating the time evolution and vertical structure of the
tidal flow, which was dominant in this case as winds were light throughout the
observational period. The motion is largely barotropic with a frictional boundary
layer near the seabed which is well reproduced by the model. To learn more about the
TC model and run it on short and seasonal time scales, go to the topic website.
7.2
Comparison with observations of turbulence
......................................................................................................................
A more important question in the present context is how well the model performs in
representing turbulent mixing. Accurate simulations of the turbulence are vital if the

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search