Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
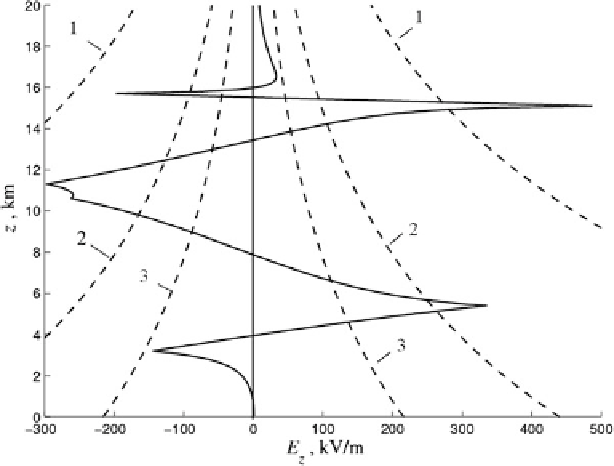
Fig. 3.17
ThesameasinFig.
3.4
but for the thunderstorm QE field preceding a GJ discharge
(Surkov and Hayakawa
2012
)
patterns of GJs are similar to inverted images of conventional
CG (Pasko
2010
;
Neubert et al.
2011
). Despite this similarity the other parameters of GJs differ
significantly from those of standard
CG. For example, a GJ recently observed by
Cummer et al. (
2009
) was estimated to transfer the negative charge of
144 C from
the thundercloud to the lower ionosphere. This value is much greater than a typical
charge
5-10 C lowered to the ground by a normal
CG stroke. Additionally,
the onset time of the GJ current was about 30 ms which is much greater than that
(
5 s) due to the stroke. This kind of GJ can be referred to as the class of negative
cloud-to-ionosphere discharge (
CI)
The first documented event of positive cloud-to-ionosphere discharge (
C
CI) has
been recently observed by van der Velde et al. (
2010
) during winter thunderstorms
in the Mediterranean. This event is characterized by the current peak value of
3:3 kA and by short duration of 120-160 ms. This
C
CI discharge was estimated to
lower negative charge
136 C down from the ionosphere to the positively charged
origins in the cloud only 6:5 km tall that result in a huge charge moment change
of 11,600 C km. This event has also demonstrated that high altitudes are not a
necessary condition for initiation of GJs.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search