Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
0.015
1
0.01
2
0.005
0
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
t
, s
Fig. 7.7
A model calculation of temporal variations of the normalized potential of elastic
displacements (Eq. (
7.106
)) resulted from an underground explosion. The lines 1 and 2 correspond
to the values of stress relaxation time t
r
D
0:3 sand0:03 s, respectively
In the theory of underground explosions another formulation of the boundary
problem is accepted. In general case the estimation of the mechanical effect of
the underground explosion is based on the set of equations describing the fracture
process and the motion of broken rocks in the vicinity of the explosion and together
with equations for dynamics of the surrounding elastic media. The method of
solving such a problem is rather complicated and we do not go into details. The
interested reader is referred to the texts by Chadwick et al. (
1964
) and Rodionov
et al. (
1971
) or other topics for a more complete treatise on mechanical processes
associated with underground explosions.
In the simple model the radial component of the stress tensor at the boundary of
the crushing zone is considered as a given function which depends on mechanical
strength of the rock, depth of explosion, and other parameters. For example, the
temporal variations of the radial stress at the boundary r
D
R
0
can be taken in the
following form:
s
rr
.R
0
;t/
D
ŒP
0
C
.P
P
0
/ exp .
t=t
r
/;
(7.42)
where P
stands for the constant of the order of tensile or compression strength, P
0
is approximately equal to the lithostatic pressure at the depth of the explosion and
t
r
is the stress relaxation time. Notice that the minus sign in Eq. (
7.42
) corresponds
to the compression stress.
The components of the stress tensor can be expressed through the radial
displacement at the boundary r
D
R
0
. The solution of this problem is found in
Appendix G. In Fig.
7.7
, we plot the time dependence of the normalized potential
given by Eq. (
7.106
). This function has a sharp front followed by damped vibrations


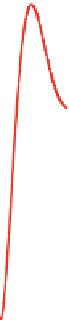












Search WWH ::

Custom Search