Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2.4
Reconstruction of the sequence of tectonic impact on the rocks of Lakatnik Karst Region
Site
Neotectonic and
recent
Method
Origin
Late Cimmerian
Pyrenean
Electrical
anisotropy
a
b
Shear
joints
I
a
b
II
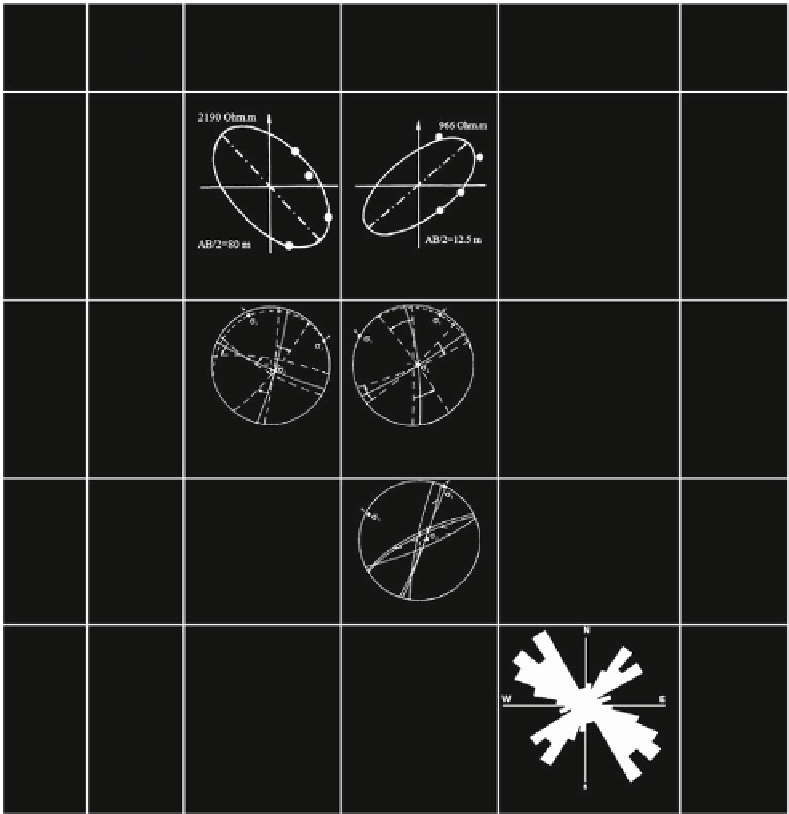
Better expressed is the eccentricity of the ellipse of
electrical anisotropy near the surface. At site No. E2,
the most intensive karstification is determined for the
first 10-15 m. It is well seen, that the long axis of the
anisotropy for AB/2 = 12.5 m is oriented NE-SW
and it can be interpreted as reflection of the com-
pression during the Pyrenean Tectonic Phase, realized
through a number of thrusts (see Fig.
2.34
), and cre-
ating conditions for opening of fractures along the
same direction, and consequently their erosion and
karst formation.
The
1. The first tectonic deformation of the whole Trias-
sic carbonate rock complex is probably related to
forces causing the overthrusting movements along
the longitudinal faults of Milanovo Karst Basin
(diagram Ia on Table
2.4
). Following the studies
of Tronkov (
1965
) it can be accepted that the
deformations were a result of the Late Cimmerian
Tectonic Phase at the end of the Jurassic period. It
coincides with the tectonic stress field of the same
age, reconstructed northward in Vratsa Karst
Region (see Table
2.3
, site No. 5). Conditions for
opening of NW oriented fractures were created.
But this is not related to the initial time of draining
conclusions
about
the
reconstructed
stress
fields and the origin of the karst system are: