Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
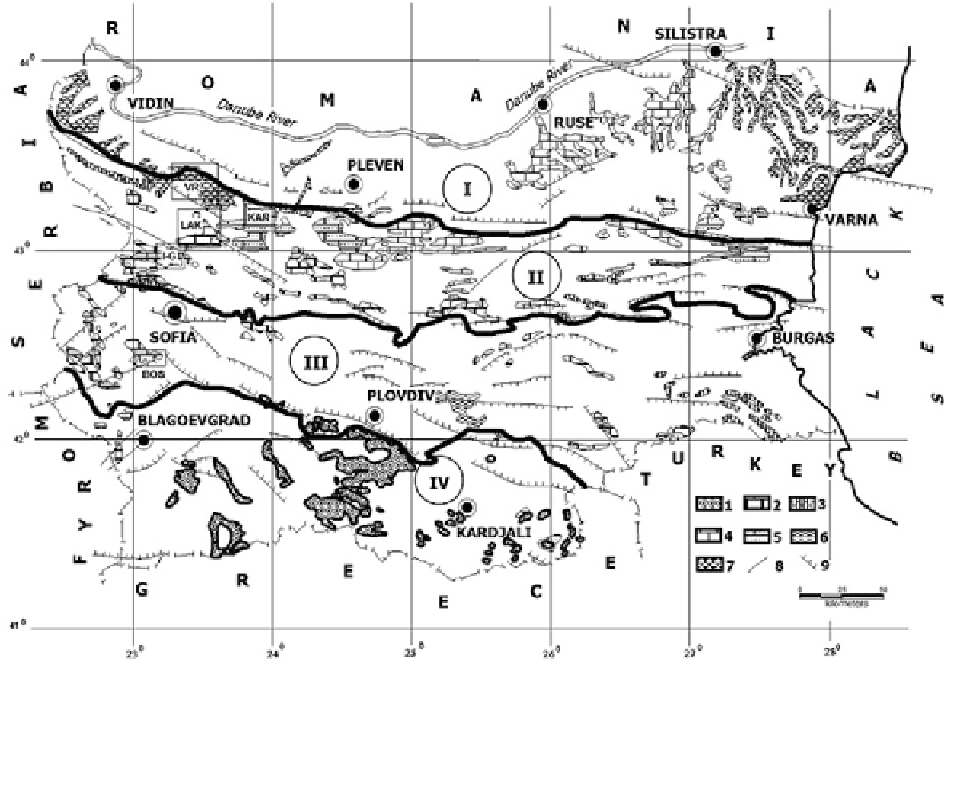
Fig. 2.29
Outcrops of karstified rocks on the territory of
Bulgaria and principal karst zones, according to Popov (
1982
)
Main regions: I—Danube Plain (Moesian platform); II—Stara
Planina
2—Triassic limestones; 3—Jurassic limestones; 4—Upper
Cretaceous limestones; 5—Maastrichtian limestones; 6—
Paleogene limestones; 7—Sarmatian limestones; Faults: 8—
strike-slip or undetermined type of movement; 9—normal
(Balkan)
Zone;
III—Intermediate
Zone;
IV—Rila-
Rhodopes
Zone
Karstified
rocks:
1—Proterozoic
marbles;
The regions differ with respect to their cave and
karst development, and on these grounds each of them
was further subdivided into several karst districts. The
Danube Plain has been discussed in Sect.
2.2
by the
study of the area of Orlova Chuka Cave amd exam-
ples from the other regions are also presented .
region; LAK—Lakatnik karst region; I-G—Iskrets-
Gubesh karst region. Their relative position is marked
in Fig.
2.29
.
Vratza Karst Region (VR)
Vratsa Karst Region, situated in the northern part of
Western Balkan Mountain, is formed in deformed
limestone layers of Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous
age. The faults have been of important role for the
development and evolution of the karst system.
Studies on the tectonic stress fields (Fig.
2.30
) were
performed principally on Vratsa Block during spele-
ological expeditions in 1985 and 1986 (analyses of
the fracturing) and the preliminary results were pub-
lished later (Chanov
1988
). New data were included
in this study, based on studies of striations on slic-
kensides, electrical anisotropy, as well as reference on
fault-plane
2.3.2.1 Western Balkan Mountain
Western Balkan Mountain (Western Bulgaria), part of
Stara Planina Zone, is known with important karst
systems draining significant quantities of fresh water.
This is an expressed mountainous area. The altitudes
of the main ridge vary between 1,000 and 2,000 m,
and the lowest part in Iskar River gorge is at
300-400 m. From hydrogeological view, six inde-
pendent karst regions are distinguished in Western
Balkan Mountain (Benderev et al.
2005
). Case studies
will be presented for three of them: VR—Vratsa karst
solution
from
an
earthquake
in
the