Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
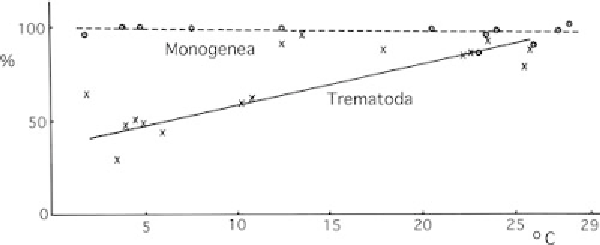
Figure 3.2. A comparison of host ranges of ectoparasitic Monogenea and
endoparasitic Digenea (trematodes) of marine teleost fish at different latitudes. Host
ranges of gill Monogenea (o) and trematodes (x). Ordinate: % of species in a survey
restricted to one or two host species. Abscissa: mean annual surface temperatures in
8C. Host ranges of Monogenea are more or less the same at all latitudes, whereas host
ranges of trematodes are much wider at high than at low latitudes. However, the
apparent increase in host ranges at high latitudes in trematodes disappears when
correction is made for intensity and abundance of infection in different host species,
i.e., parasite species have similar host specificity at all latitudes. From Rohde (
1978c
).
Reprinted by permission of Springer-Verlag.
species than cold-water fish (Figure
3.2
). Sample size was not responsible
for these findings. Prevalence of infection tends to be greater in tropical
fish. In other words, niche width (at least along the dimensions, host
range, microhabitat width, and prevalence of infection) is not narrower in
species-rich communities. One reason is that many niches (microhabitats)
are empty. Also, many and perhaps all host species could accommodate
more parasite species, and fish with few ectoparasites do not have more
endoparasites, which makes the argument invalid that a host is a func-
tional unit and that the carrying capacity of a host with few ectoparasite
species might be used by parasites in other habitats.
Competitive exclusion and its prevention by spatial/temporal
heterogeneity
A direct consequence of limiting similarity is competitive exclusion, i.e.,
the complete displacement of one species by another, competing species.
This is expressed as Gause's principle, according to which (in its original
and widely used form) species using the same resource cannot coexist (see
previous sections), (e.g., Levin
1970
; May
1981
). In accordance with this
principle, in an absolutely homogeneous world with a single resource,