Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
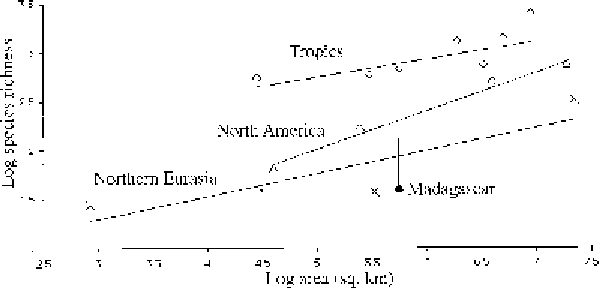
Figure 9.8. Effects of latitude, area, and continent (history) on richness of fish species
in some freshwater systems. From left to right, Tropics: Lake Malawi, Malaysia,
Thailand, Indonesia excluding Papua New Guinea, India, Congo basin, Amazon
basin, South and Southeast Asia. North America: NWWisconsin, North American
Great Lakes, North America. Eurasia: Lake Constanze, Lake Baikal, Finland, former
USSR. Madagascar (strictly freshwater species indicated by a filled circle, bar
represents number of marine species regularly or sporadically invading freshwater).
Note the generally increased diversity in the Tropics, the effect of area, the greater
richness in North America than in Europe, and the abnormal species poverty in
Madagascar, likely to be due to the long isolation from a large continent. Data for
Amazon and Congo basins from Rosenzweig and Sandlin (
1997
). Data for
Madagascar from Stiassny and Raminosoa (
1994
), for Finland and NWWisconsin
fromTonn et al.(
1990
). Data for Lake Constanze fromGeller and G¨de(
1989
). Data
for USSR and Lake Baikal from Sheremetyev, personal communication. All other
data from various references in Rohde (
1997
,
1998a
).
freshwater fishes, it seems that highest diversity is found in tropical lakes
with highest productivity (although data are insufficient to correct for
area along a latitudinal gradient). This, of course, does not ''prove'' that
productivity ''explains'' latitudinal gradients in species diversity. There are
other covariables, such as temperature, solar radiation, and seasonality,
that may be responsible. Also, as pointed out by Rohde (
1998a
), high
productivity may well be the result rather than the cause of great species
diversity.
Dobson et al.(
2000
) have investigated the relationship between pri-
mary productivity and species richness in 33 North American lakes. They
considered diversity of phytoplankton, rotifers, cladocerans, copepods,
macrophytes, and fish. Primary productivity was measured as g C/m
2
per
year,
14
C estimate. All taxa showed a significant quadratic response to
increased annual primary productivity, when lake area was taken into