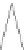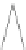Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
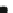
(a)
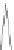
(b)
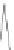
(c)
K
3
gadget
C
4
gadget
K
4
gadget
kite
gadget
(d)
(e)
Fig. 2.
(a) A radius-2 star. (b) A 1-connected extended degree-3 spider. (c) A 2-connected extended
degree-3 spider (containing a kite gadget). (d) A generalized caterpillar. (e) A fat caterpillar.
Lemma 5.
Let
G
be agraph such thateither:
(
i
)
G
is a radius-2 starthatisnot a
generalized caterpillar; or
(
ii
)
G
contains a cycle of lengthatleast
4
;or
(
iii
)
G
is an
extended degree-3 spider thatisnot ageneralized caterpillar. Then
G
∈
EAP
.
Theorem 2.
Aplanar graph
G
is an EAPgraph if andonly if it is a fatcaterpillar.
Proof.
“Only if part”. If
G
is an EAPgraph, then by Lemma 3 it is also AEP and
therefore it is either a radius-2 star, or an extended degree-3 spider, or a generalized
caterpillar. By Lemma 5,
G
must be a generalized caterpillar and cannot contain a cycle
of length four. Hence it must be a fat caterpillar.
“If part”. Let
G
be a fat caterpillar. We prove that
ihs
(
G
)=1.Wedefinea
y
-leveling
Y
of
G
as follows. For each path vertex
v
i
(1
≤ i ≤ k
)of
G
we set
Y
(
v
i
)=2
i
. For each
tip vertex
u
i
(1
≤ i ≤ k
)of
G
we set
Y
(
u
i
)=
Y
(
v
i
)+1. For each degree-one vertex
j
w
i,j
we set
h
i
+1
(
j
=1
,
2
,...,h
i
). Observe that the vertices of
G
have been assigned a different value and therefore
Y
(
w
i,j
)=
Y
(
v
i
)+
Y
is a valid
y
-leveling. Consider
now an arbitrary
x
-leveling
X
. We show that
ihs
(
ʓ
(
X
,
Y
)) = 1, which implies that
ihs
(
G
)=1. Consider a stabber
at
l
,
l
∈
R
.If
l<
2 or
l>
2
k
,then
does not intersect
any edgeof
ʓ
(
k
,then
passes throughvertex
v
i
and it
intersects only the edges incident to
v
i
, which are not independent. If
l
=2
i
+1for
1
X
,
Y
).If
l
=2
i
for 1
≤
i
≤
1,then
either intersects only the edge (
v
i
,v
i
+1
) (if the tip vertex
u
i
does
not exist), or it intersects the three edges (
v
i
,v
i
+1
), (
v
i
,u
i
),and(
u
i
,v
i
+1
) (if the tip
vertex
u
i
exists) no two of which are independent. If 2
i<<
2
i
+1for 1
≤
i
≤
k
−
1,
then
intersects the edge (
v
i
,v
i
+1
), possibly the edge (
v
i
,u
i
), and possibly some of
the edges (
v
i
,w
i,j
) (
j
=1
,
2
,...,h
i
). No two of these edges are independent. Finally,
if 2
i
+1
<l<
2
i
+2for 1
≤
i
≤
k
−
1,then
intersects the edge (
v
i
,v
i
+1
) and
possibly the edge (
u
i
,v
i
+1
), which are not independent. Thus, no stabber intersects
two independent edges in
ʓ
(
≤
i
≤
k
−
X
,
Y
) and therefore
ihs
(
ʓ
(
X
,
Y
)) = 1. It follows that
ihs
(
G
)=1and, by Lemma 4,
G
∈
EAP
.