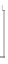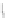Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
A User Study on the Visualization of Directed Graphs
Walter Didimo
1
, Fabrizio Montecchiani
1
,Evangelos Pallas
2
, and Ioannis G. Tollis
2
1
Dip. di Ingegneria, Universit`adegli Studi di Perugia, Italy
2
University of Crete and Institute of Computer Science-FORTH, Greece
(a) HD
(b) OD
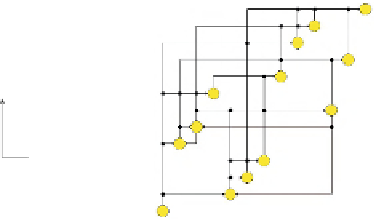
(c) OOD
(d) MR
Fig. 1.
Different drawing styles for directed graphs
In a node-link visualization of a directed acyclic graph it is desirable that edges flow
in a common direction (say upward) according to their orientations, as in
Hierarchical
Drawings(HD)
(see, e.g., [3]). More general requirements are that the number of edge
crossings, the number of edge bends, the drawing area, etc., are kept low. These are
well addressed by
Orthogonal Drawings(OD)
,whereedges are chains of horizontal
and vertical segments (see, e.g., [4]). Unfortunately, OD algorithms do not control the
flow of the edges in a desired direction.
Overloaded Orthogonal Drawing (OOD)
is a
recent visualization paradigm conceived for drawing directed graphs, that merges and
enforces the benefits of HD and of OD [2]. Indeed, edges are still represented using
only horizontal and vertical segments, and if the digraph is acyclic, any directed edge
(
u,v
) is drawn as an upward-rightward polyline consisting of one bend point (
v
is
above and to the right of
u
). Also, adjacent edgesegments can partially overlap to draw
graphs with arbitrary vertex degree. We present the results of a user study aimed at
measuring the usability of OOD on directed graphs against HD and OD. Moreover,
we consider
Matrix-based Representations(MR)
. Indeed, a user study on undirected
graphs [1] suggests that MR are more suitable than node-link diagrams computed with
force-directed algorithms to perform some simple tasks when the size of the graph
increases, but remains relatively small. Thus, we also aim to understand whether OOD
maintains the same readability properties as MR with respect to user's tasks similar to
those considered in [1], but tailored to directed graphs. See Figure 1 for an illustration.
An extended abstract of this work has been presented at the 5
th
Conference on Information,
Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA 2014). Research supported in part by the MIUR
project AMANDA: Algorithmics for MAssive and Networked DAta, prot. 2012C4E3KT 001.