Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
v
0
,
3
v
0
,
2
v
0
,
1
v
3
,
0
v
2
,
0
v
1
,
0
v
0
,
0
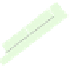
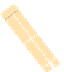
(a) (b)
Fig. 3. (a)
Square grid
S
3
,
3
; for thick edges, the moving sets are indicated by the framed vertices
(b)
USqPCR
ˆ
of
S
3
,
3
with illustration of modification step.
We claim that
ˆ
is a USqPCR of
S
m,n
cs
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
=1
−
ʵ
for all (
u,v
)
∈
E
S
and
sp
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
,d
≥
ʵ
for all (
u,v
)
/
∈
E
S
and the two directions
d
parallel to the
square'ssides:
d
1
:=
0
and
d
2
:=
1
Consider a vertex
v
and its fourneighbors. Each contact is realized by one side of
ˆ
(
v
).
By definition of
ˆ
, the characteristic corners differ by
±
ʵ
,
±
−
1
. Hence, the squares
are disjoint and cs
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
=(1
−
ʵ
),forall(
u,v
)
∈
E
S
. Consider a non-edge
E
S
. The characteristic corners of
ˆ
(
u
) and
ˆ
(
v
) differ by
a
ʵ
+
b
−
1
with
(
u,v
)
/
∈
2. This implies that sp
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
,d
i
≥
a, b
∈
Z
and
|
a
|
+
|
b
|≥
ʵ
for
i
∈{
1
,
2
}
.
We now define the moving sets and translation vectors: For
e
=(
v
i,j
,v
i
+1
,j
),we
set
d
(
e
):=
d
1
=
0
and
M
(
e
):=
{
v
k,j
∈
V
|
k>i
}
,otherwise
e
=(
v
i,j
,v
i,j
+1
),
we set
d
(
e
):=
d
2
=
1
and
M
(
e
):=
{
v
i,k
∈
V
|
k>j
}
. For simplification, we
define
E
i
:=
{
e
∈
E
|
d
(
e
)=
d
i
}
for
i
∈{
1
,
2
}
and assume wlog
n
≥
m
.The
idea is to remove each contact of
e
E
by translating
M
(
e
) in direction
d
(
e
).The
integer
r
i
(
v
) describes how often
v
is moved in direction
d
i
,thatis
r
i
(
v
):=
∈
|{
e
∈
E
∩
E
i
|
v
∈
M
(
e
)
}|
. Observe that
r
i
(
v
)
≤
n
for
i
∈{
1
,
2
}
and
v
∈
V
. Choosing
ʴ<
n
min
{
ʵ,
1
−
ʵ
}
the following mapping is a USqPCR of
G
ↆ
S
m,n
:
2
)
ˆ
(
v
)=
ˆ
(
v
)+
r
1
(
v
)
ˆ
:
V
ₒP
(
R
·
ʴd
1
+
r
2
(
v
)
·
ʴd
2
.
We verify that
ˆ
is a USqPCR of
G
by showing three properties: Let (
u,v
)
/
∈
E
S
. Recall
that sp
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
,d
i
gives the maximum translation step
ʻ
such that
ˆ
(
u
) and
ˆ
(
v
)
remain interiorly disjoint when either one of them is translated by
ʻd
i
. By construction
r
i
(
w
)
ʴ
sp
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
,d
i
for
w
≤
nʴ < ʵ
≤
∈{
u,v
}
and
i
∈{
1
,
2
}
. Consequently,
ˆ
(
u
) and
ˆ
(
v
) remain disjoint.
Let (
u,v
)
E
i
,then
ˆ
(
u
) and
ˆ
(
v
) have a contact segment parallel to
d
i
+1
of
length cs(
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
))
∈
≥
1
−
ʵ
. Hence, translations in direction
d
i
+1
have no effect on
the contact: cs
ˆ
(
u
)
,ˆ
(
v
)
≥
cs
ˆ
(
u
)
, ˆ
(
v
)
−
nʴ >
0.Wlog
we suppose that
ˆ
(
u
) is left or below of
ˆ
(
v
), then by definition of the moving sets:
r
i
(
u
)
r
i
+1
(
v
)
ʴ
≥
1
−
ʵ
−
r
i
(
v
). This implies that
ˆ
(
u
) and
ˆ
(
v
) remain interiorly disjoint.
Since the translation vector
d
i
is not parallel to the contact segment, the contact
remains iff
r
i
(
u
)=
r
i
(
v
). By definition, this is the case iff (
u,v
)
≤
∈
E
. Note therefore,