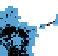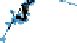Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
untangle each graph. Specifically, participants were shown an example starting layout
and untangled layout(showninFig. 3) and told “to untangle the graph. This involves
moving parts of the graph to new locations in order to make the underlying structure
of the graph clear”. Following this, the untangling trials began. The display provided
instructions informing the participant of the conditions of the next trial (for example,
physics colored
). The participant clicked the mouse to begin the trial and the display
changed to show the initial graph layout. The participant then had two minutes to best
untangle the graph. After two minutes, the video wall went blank while the next trial
was loaded. After eight trials the participants were asked to complete the subjective
questionnaire and the session was concluded.
(a)
(b)
(c)
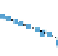
Fig. 3.
(a) The starting layoutforgraph B. (b) Layoutforgraph B using stress minimization. (c)
Final layout created by one of the participants.
5R su s
Sixteen participants completed the experiment, recruited from staff and students from
the University of South Australia, and the general public. Participant ages ranged from
23 to 57, with a mean age of 33. Five of the participants were female, and all but
one of the participants were right handed. The mean score for the graph theory quiz
was 74.22% (std. dev 25.19). Pearson Correlation analysis was performed to see how
quiz score affected results. A significant correlation was found between quiz score and
changeinedge crossings for the normal/color condition,
r
=
.
876
,.
453]
,
p
<
0
.
05. Quiz results did not affect any other conditions. All other quantitative results were
analysed using a 2x2 repeated measures ANOVA.
−
.
505[
−
5.1
Mouse Usage
There was a significant main effect on interaction mode,
F
(1
,
15)=36
.
586
,
p
<
0
.
001.
There was significantly less mouse travel in the
physics
condition compared to
normal
,
with 59294.661mm (SE 5001.180) of mouse travel for the
physics
condition compared
to 76227.881mm (SE 4153.657) for the
normal
condition. The graph coloring did not
produce a significant effect on mouse travel, and there was no significant interaction
between interaction mode and graph coloring.
There was a significant main effect on the interaction mode,
F
(1
,
15)=6
.
279
,
p
<
0
.
05. Participants made fewer mouse clicks for the
normal
condition than
physics
, with