Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
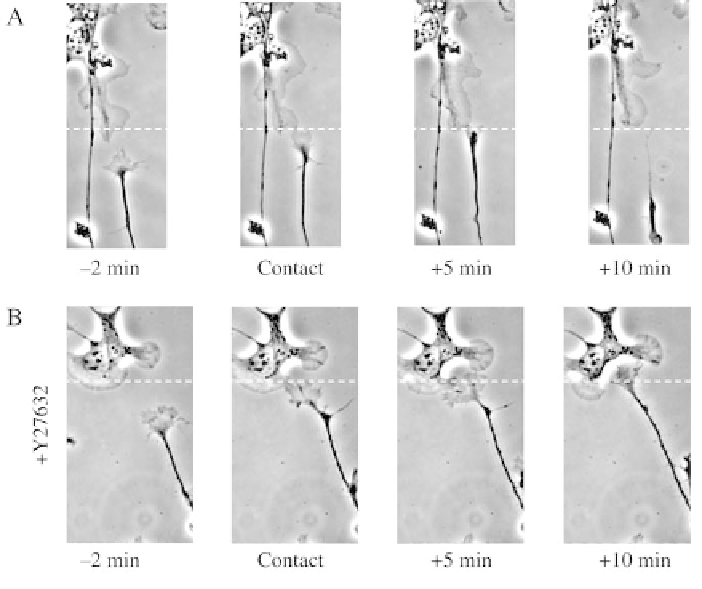
Figure 4.4 Ephrin-A ligands on the surface of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts induce Rho kinase
mediated growth cone collapse and axon retraction. (A) A RGC growth cone in culture
encounters an ephrin-A expressing fibroblast. Times shown are times after contact of the
cells. (B) Time-lapse stills of a co-culture experiment in which 10 mM Y27632 has been
added to the bathing medium. Times indicated are times after contact is seen to occur
between the two cells
By addition of soluble extracellular portions of A-class Eph receptors we
block the interaction between ephrin-A ligands expressed on the surface of the
fibroblast cell, and EphA receptors on the RGC growth cone. Addition of
soluble EphA5 prevents the growth cone collapse and axon retraction seen in
the RGC, and the repulsive response in the fibroblast cell (data not shown),
confirming that these responses are directly mediated by Eph receptor-ephrin
interaction.
The presence of the Rho associated kinase inhibitor, Y27632, in the co-
culture assay dramatically prevents the rapid retraction of the axon we
observe in response to contact with a cell expressing surface ephrin, and delays
the loss of lamella (Figure 4.4B). In the presence of Y27632 the lamella is lost
on average 11.6+4.8 minutes after contact with the ephrin-expressing
fibroblast (n ¼ 13), as compared with 5.9+2.6 minutes in the control situation