Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
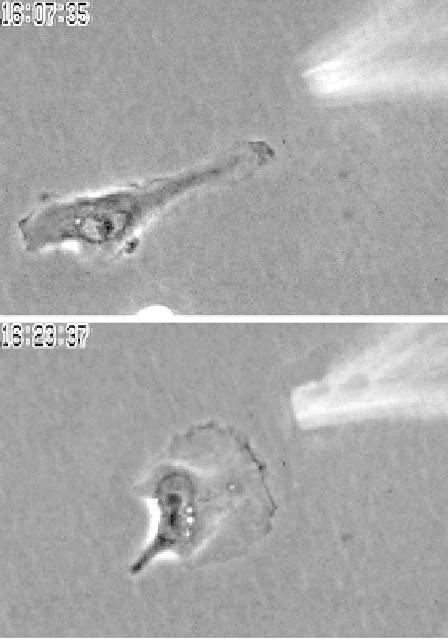
Figure 11.2 Carcinoma cells are chemotactic to EGF in vitro. When MTLn3 cells in
culture are presented with a pipette filled with EGF they rapidly polarize toward the pipette
and move up the concentration gradient. Two frames from a time lapse movie taken 16 min
apart illustrate the pipette following activity. In the top frame the cell is moving to the left
as the pipette is dropped into the field while in the the bottom frame the cell has reversed
direction and is moving up the EGF gradient toward the pipette. (This figure is adapted
from Bailly et al., 1998)
enhancing metastatic capability in addition to the well-characterized effects of
EGF receptor signalling on mitogenesis.
We have tested the hypothesis that chemotaxis to vessels is an important
form of egress of carcinoma cells from the primary tumour. We challenged
cells within live primary mammary tumours in intact rats using microneedles
filled with matrigel and containing chemoattractants to mimic chemotactic
signals from blood vessels and associated cell layers (Wyckoff et al., 2000).
These microneedles, when placed into a mammary tumour, collect large
numbers of cells in short time intervals (Figure 11.3). This process is active
involving the motility of the cells into the needle. In addition, the migration is
dependent on the presence of extracellular matrix within the needle, is greatly