Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
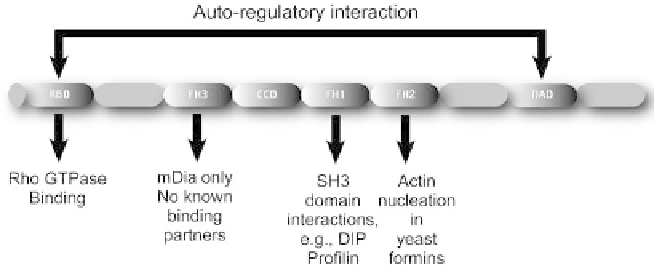
Figure 8.3 The predicted domain structure of mDia (mammalian diaphanous).
RBD
¼
Rho-binding domain; FH1
¼
poly-proline rich formin homology domain 1,
which binds to SH3 domains; FH2
¼
formin homology domain 2, which shows actin
nucleation activity in yeast formins; FH3
¼
formin homology domain 3; CCD
¼
coiled-coil
domain; DAD
¼
Dia auto-regulatory domain, which interacts with the RBD to form the
inactive conformation of the protein
The FH1 domain contains a proline-rich module that interacts with several
Src Homology 3 (SH3) domain-containing proteins (Krebs et al., 2001),
linking formins to tyrosine kinase signalling pathway proteins. Satoh and
Tominaga show the FH1 domain to be involved in the interaction between
mDia1 and Dia-interacting protein (DIP), a ubiquitously expressed protein
which is involved in stress fibre formation and to affect focal adhesion
turnover through activation of Src (Satoh and Tominaga, 2001).
Evidence for Arp2/3 complex-independent nucleation focuses on the
formation of actin cable structures and unbranched actin filaments. This
does largely suit the idea that stress fibres and lamellipodia are formed by
different nucleation mechanisms, but it is dicult to exclude the concept that
the Arp2/3 complex may be recruited to sites of unbranched filament
formation and inhibited from forming 708 branches or that branches are
short-lived and may be remodelled into other types of structures.
The role of Ena/VASP proteins
The architecture of actin arrays appears to be regulated by the Ena/VASP
proteins, possibly providing some of the diversity of structures observed in
lamellipodia, filopodia and other actin-rich protrusions. The Ena/VASP
proteins are a family that share two domains termed Ena/VASP homology
domains (EVH1 and EVH2). The family consists of several members;
vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) originally identified as a
substrate for cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases, Drosophila enabled
(Ena) and its mammalian homologue, Mena and the Ena/VASP-like protein