Java Reference
In-Depth Information
1400
n!
2
n
2n
2
5nlogn
1200
20n
1000
800
600
10n
400
200
0
0
10 20 30 40 50
2
n
2n
2
n!
400
20n
300
5nlogn
200
10n
100
0
0 5 10 15
Inputsizen
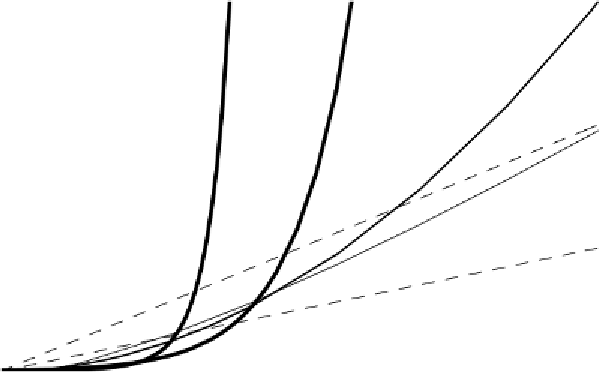
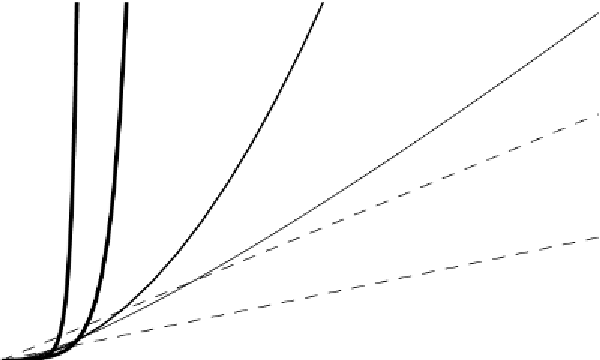
Figure3.1
Two views of a graph illustrating the growth rates for six equations.
The bottom view shows in detail the lower-left portion of the top view. The hor-
izontal axis represents input size. The vertical axis can represent time, space, or
any other measure of cost.
operation for variable sum. We can assume that incrementing takes constant
time; call this time c
2
. (We can ignore the time required to initialize sum,
and to increment the loop counters i and j. In practice, these costs can
safely be bundled into time c
2
.) The total number of increment operations
is n
2
. Thus, we say that the running time is T(n) = c
2
n
2
: