Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
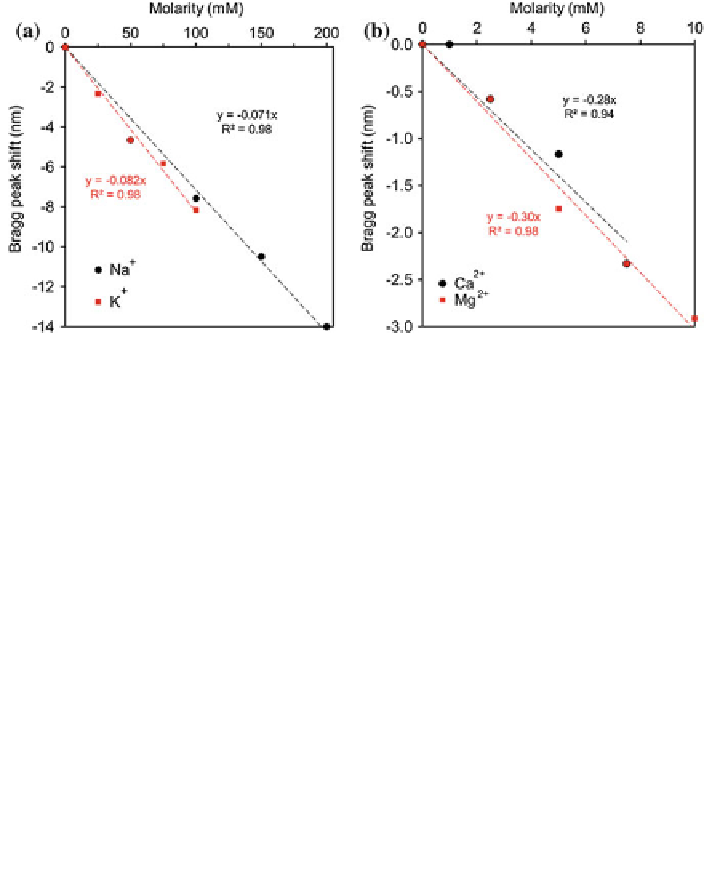
Fig. 3.16 Interference due to monovalent and divalent metal ions in holographic pH sensor
response at 24
C. a Na
+
and K
+
, b Ca
2+
and Mg
2+
ions
°
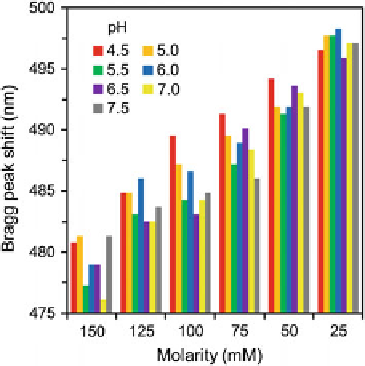
Fig. 3.17 Bragg peak shifts due to pH and Na
+
ion concentration as the molarity was changed in
pHEMA matrices with residual MAA remaining from its manufacturing process
3.4.5 Sensing pH in Arti
cial Urine
To demonstrate the utility of the holographic pH sensor, a clinical application to
analyse acid-base balance in arti
cial urine samples is described. Urine pH in a
healthy individual is in the range of 5.0
9.0 [
46
]. Analysis of urine pH has diag-
nostic utility in, for example, the evaluation of urinary tract infections (UTIs) [
47
]
and renal tubular acidosis [
48
]. Modi
-
cation of the urine pH allows the treatment