Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
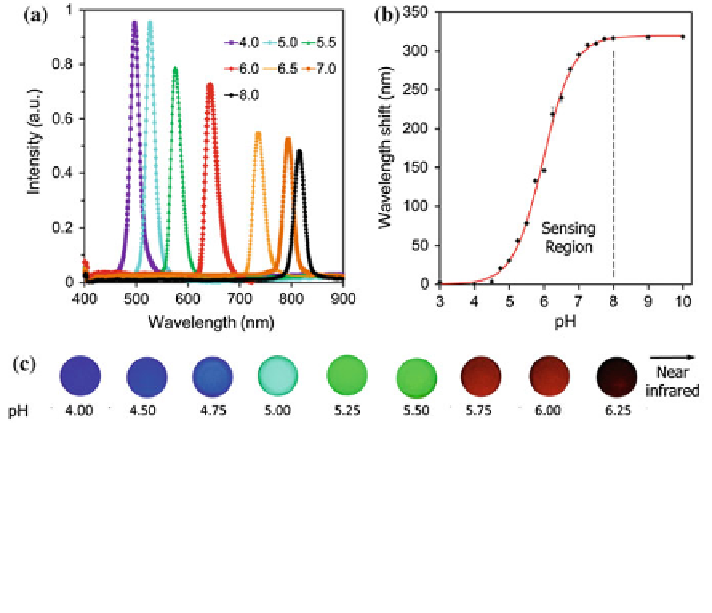
Fig. 3.14 Tuning the holographic pH sensor (6 % MAA) fabricated through in situ size reduction
of Ag
0
NPs. a Visible-near-infrared diffraction spectra of the holographic sensor swollen by
different pH values using phosphate buffers (150 mM) at 24
°
C. The smallest Bragg peak was at
495 nm and the largest was at 815 nm
a change of 165 %. b Sensor response over three trials.
The apparent pK
a
value was calculated as 5.98 using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
c Photographs of the sensor immersed in phosphate buffers of pH 4.00
—
6.25. The images were
taken under white light illumination. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [
18
] Copyright 2014
Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH&Co. KGaA, Weinheim
-
methacrylate (pK
a
= 8.40) [
20
]. In order to extend the range, a mixture of ionisable
monomers may be co-polymerised. Such hydrogels can also be functionalised to be
highly selective to a range of stimuli [
24
,
38
45
]. Figure
3.15
illustrates the
summary of holographic pH sensors fabricated on different substrates. The
photochemical patterning through in situ size reduction of Ag
0
NPs was comparable
to the previously developed silver halide chemistry-based holographic pH sensors.
However, the maximum achievable Bragg peak shifts differed in three cases
(Fig.
3.15
). This might be attributed to the error in controlling MAA concentration
and degree of crosslinking in each formulation.
-
3.4.3 Interference Due to Metal Ions
Biological samples such as urine and blood contain a mixture of ions and other
potential interferents. The effect of these interferents on the holographic pH sensors
was evaluated. Control experiments were conducted to assess the sensitivity of
pHEMA (no MAA) to Na
+
,K
+
,Mg
2+
and Ca
2+
ions. Na
+
ions are the most