Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
photonic structure along the pAAm matrix
'
s transversal section con
ned within a
m
2
area. The colours from blue to red represent the phase of the elec-
tromagnetic
20
×
10
μ
ected 3
and the refracted waves of light 4. The diffracted wave 2 observed at angles away
from specular re
field. Fresnel
'
s law describes the paths of the incoming 1,re
fl
fl
ection, obeying Bragg
'
is law,
k
peak
¼
2
K
sin
ðÞ
, where
k
peak
is the
wavelength of the
first order diffracted light at the maximum intensity in vacuo, n
0
is the effective index of refraction of the recording medium,
ʛ
is the spacing
between the two consecutive recorded NP layers, and
is the Bragg angle. The
offset diffraction from the device produced a narrow-band readout signal, allowing
the differentiation of small changes in optical properties of the device due to
different types and concentrations of analyte. These simulations allow designing
holographic sensors with predictive optical properties. For example, simulations
can be used to estimate the angle of diffraction or the diffraction ef
θ
ciency required
for a speci
c application.
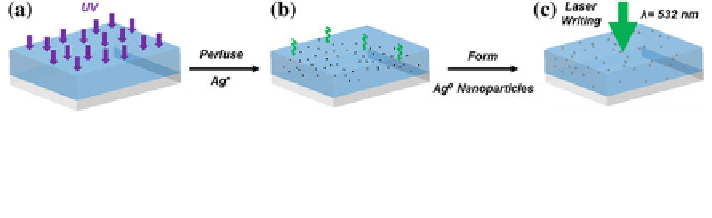
5.4 Fabrication of Holographic Glucose Sensors
The monomer mixture (5 mmol) consisted of acrylamide (AAm), N,N
-methylene-
bisacrylamide (MBAAm) and 3-APB (Table
5.2
). The solution was mixed (1:1, v/v)
with DMPA in DMSO (2 %, w/v). The mixture was copolymerised on an
O
2
-plasma-treated PMMA substrate (Fig.
5.4
a). Ag
+
ions were perfused into poly
(AAm-co-3-APB) matrix, and they were reduced to Ag
0
NPs in situ using a pho-
tographic developer (Fig.
5.4
b). A holographic sensor was formed by photochem-
ically patterning the matrix via a single 6 ns Nd:YAG laser pulse (
′
ʻ
= 532 nm,
Table 5.2 Composition of
glucose-responsive hydrogels
Monomer
Molecular weight (g/mol)
Molarity (%)
AAm
71.08
75
-
80
MBAAm
154.17
1.5
3-APB
190.99
10
20
-
DMPA
256.30
2 (wt%) in DMSO
Fig. 5.4 Fabrication of holographic glucose sensors. a Free radical copolymerisation of AAm,
MBAAm and 3-APB, b perfusion of Ag
+
ions into the poly(AAm-co-3-APB) matrix and
formation of Ag
0
NPs using a photographic developer, and c formation of diffraction gratings in
Ag
0
NP impregnated matrix