Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
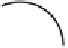
Global disable
M
esh clock
Gated c1
clock
Scan-only
latches
Local disable
enable
C2 latches
Dynamic Stop
LOGIC
FIGURE 4.5:
Clock gating in the Power5. Adapted from [
57
].
XScale core
: The Intel Xscale processor is a low-power processor boasting an impressive
DVFS range. While its low power abilities come mainly from DVFS, it is also highly optimized
for low power at the circuit and architectural levels [
58
]. The design of the processor is mostly
static CMOS logic supporting full clock stop. The processor implements three power-saving
modes (besides its extensive DVFS abilities):
Idle mode
(full clock stop via clock gating),
Standby
mode
which stops the phased locked loop (PLL) and puts the processor in reverse body bias for
low leakage, and finally
Sleep mode
, which does not even retain state.
The low-power design features of an Xscale core are detailed by Clark et al. [
58
]. At the
circuit design level, the implementation utilizes
pulse-clocked latches
instead of ordinary master-
slave latches, cutting down on clock power consumption by 30%. Pulse-clock latches do not
need explicit clock gating (as was described in Section 4.2.1 for ordinary flip-flops) and result
in less switching activity for the sequential elements they feed.
Clock pulses to drive the pulse-clocked latches are generated by distributed units called
Local Clock Buffers (LCBs), which are fed by a balanced global clock network. Clock gating
in XScale is implemented at the LCBs. Each LCB has enable signals which can stop the pulse
generation. Because of the overhead of pulse generation and clock gating, each LCB must feed
at least five latches. This is the smallest unit in the Xscale core that can be individually clock
gated.
Clock gating in the Xscale is implemented at three different levels. First, at the PLL
to implement the processor-wide Idle mode by halting all clock activity; second, at the global
clock level (GCLK) with 83 unique enable signals; third at the individual LCB level with 400
distinct enable signals [
58
]. Although no further details are disclosed for the policies to engage
clock gating, deterministic clock gating described above can be easily implemented in such a
framework.
Xscale cache
: Architecturally, the Xscale is a simple, single-pipeline, in-order processor.
The pipeline is 7-stage for integer operations, 8-stage for memory, and 9-stage when executing
the compact ARM Thumb instruction set. The pipeline is optimized for the high-frequency
operation and its low complexity makes it very power efficient.

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search