Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
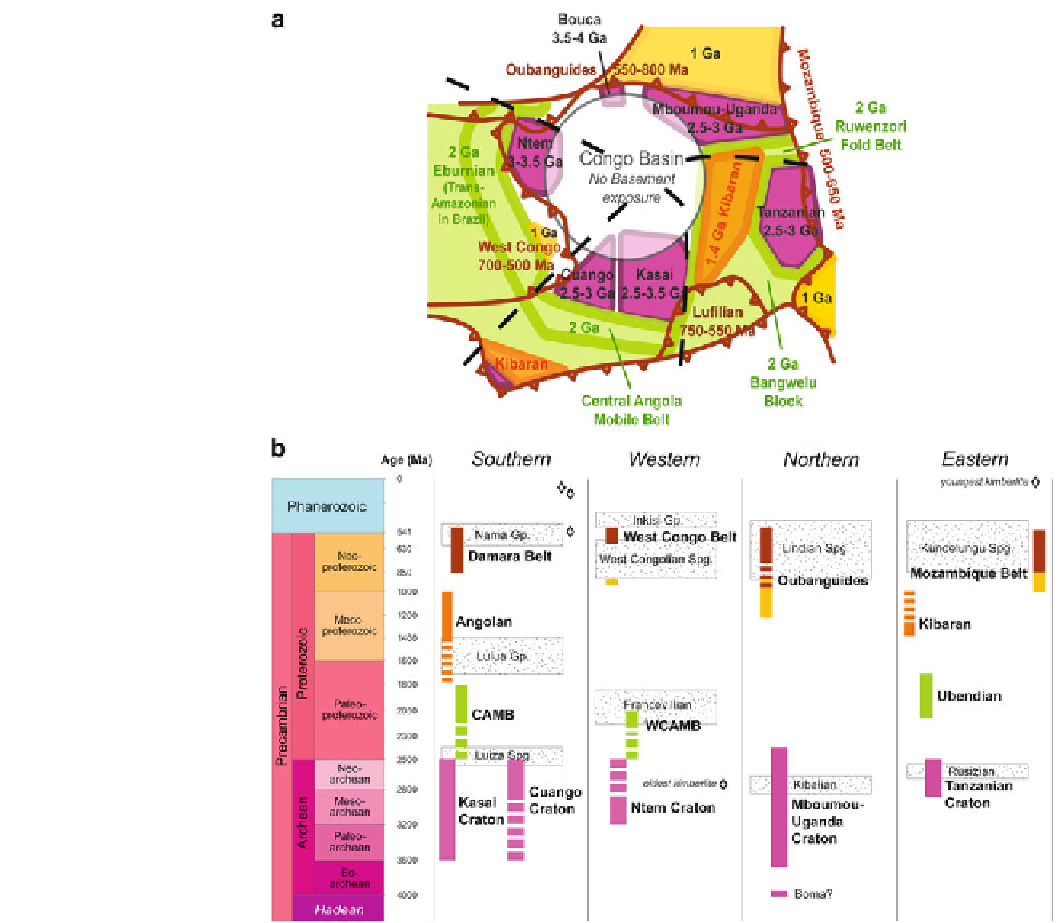
Fig. 2.3
(
a
) Sketch map of
Precambrian basement
surrounding the CB, showing the
six Archean cratonic blocks
(
purple
); Eburnian (
green
) and
Kibaran terrains (
orange
and
yellow
), and tectonic fronts of
Pan African fold-and-thrust belts
(
brown
). Possible Pan African
structures below the basin are not
shown. (
b
) Time-Space diagram
of Precambrian of central Africa.
The four regions are shown in (
a
)
(
dashed lines
) and described in
detail in the text. Dotted
rectangles in b
¼
sedimentary
sequences
(CAS) that stabilized by ca. 540 Ma (Fig.
2.1
,insetB).CAS
incorporates: the West Congo Belt of Gabon, western DRC
and northwestern Angola; the Oubanguides (or sometimes
called the Central African Fold Belt) of northern Gabon,
Cameroon and CAR; the Mozambique Belt (as part of the
southern East African Orogen) from southern Sudan, eastern
Tanzania, Kenya and Mozambique; the Lufilian Belt (Arc) in
Zambia and its extension into northwest Botswana and
Namibia (as the Damara Belt) and from there north through
the Kaoko Belt back to a link with the West Congo Belt in
northwest Angola, via parts of the Braziliano Ara¸ua´ Belt
(now) of eastern Brazil (e.g. de Wit et al.
2008
;Fig.
2.3
).
The precise connections between these Pan African Belts and
their Brasiliano counterparts are still under scrutiny (e.g.
Pedrosa-Soares et al.
2008
; IGCP-628 project, and draft
Gondwana Geological Map
2014
, Renata Schmitt Personal
communications, 2014).
Thereafter, this lithosphere of central Gondwana experi-
enced prolonged and complex long-wavelength perturbations
during multiple compression and then multiple rifting events
as it became covered by Paleozoic and Meso-Cenozoic sedi-
mentary basins—of which the CB is a prime and globally
unique example (e.g. Linol,
2013
; Linol et al., Chap.
12
of
this Topic). Unlike its early-linked Paran´ Basin (now in
Brazil), and unlike the Michigan Basin of North America to
which an over-simplified history of the CB has been frequently
compared (e.g. Hartley and Allan
1994
), Gondwana break-up
led to a CB that evolved further into a continental basin
surrounded by rifts, except along its southern margin, where
it is flanked by the southern (Kalahari) African high Plateau
underlain by the Southern African Shield (e.g. Fig.
2.4
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search