Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
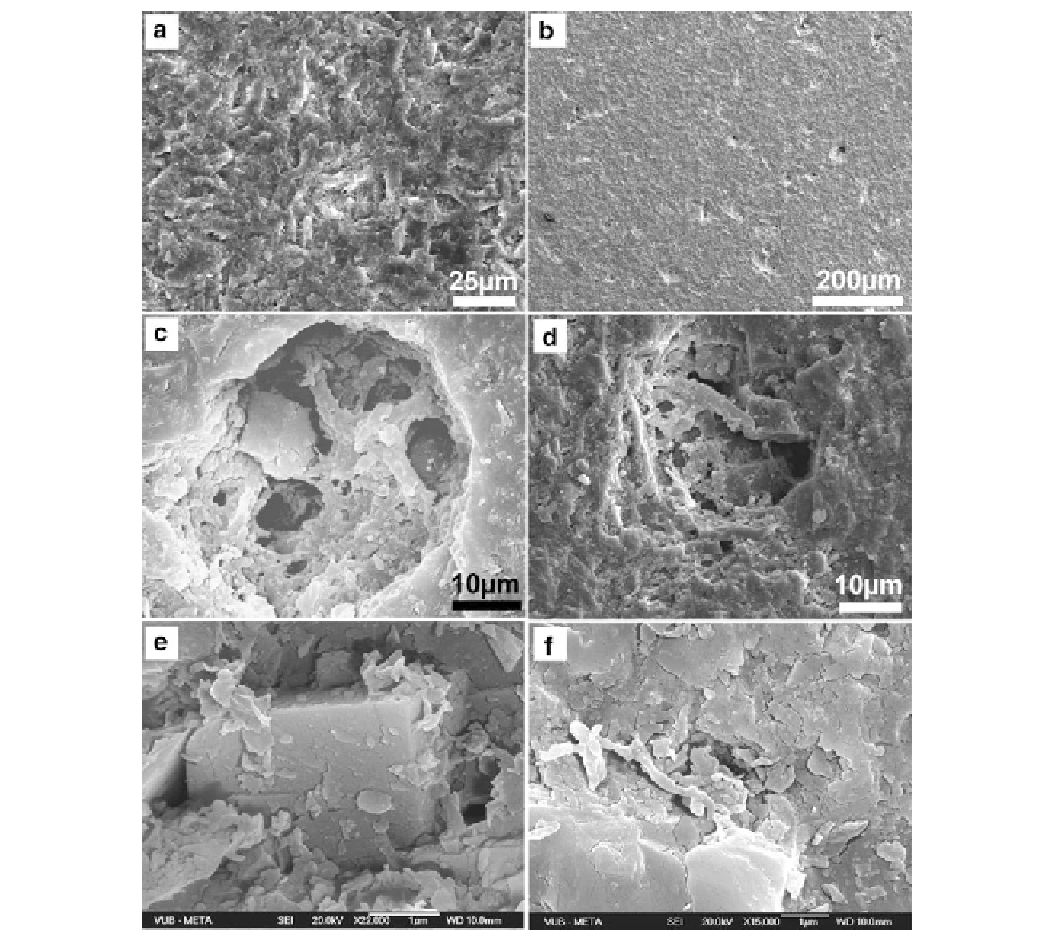
Fig.
5.4
(
a
)
Filamentous
dichotomous
bacterial
(probable
Sample MOU19, Mouila old quarry, Gabon (photo mou19-17/2007/
ap). (
d
) Small-sized (~25
cyanobacteria) ranging from 2 up to 5
m in diameter. They are partly
destroyed by a fine-grained dolomicropsar. The photograph has been
taken in a homogeneous dolomudstone layer (see Fig.
5.3f
). Sample
MOU26, Mouila old quarry, Gabon (photo mou26-63/2007/ap). (
b
)
Surface of sample MOU26 (
thin section
) under the SEM showing
numerous inframillimetric irregular to subrounded pits or
μ
m) pit in a dolomicrosparitized mudstone
(see Fig.
5.4a
). Same filaments as previous figure with diameters
ranging from 0.25 to 1
μ
μ
m. Dolomicrospar is more regular and consists
of small-sized (1-5
m) well crystallized rhombs growing from a
dolomicritic matrix. Thinner (0.1 or less micron in diameter) are
associated with the larger filaments. They exibit a discrete
barrel-
shaped cells
. Some filaments are engulfed in the dolomicrospar. Sam-
ple MOU26, Mouila old quarry, Gabon (photo mou26-20/2007/ap).
(
e
) Quadratic dolomite crystal probably derived from a calcium oxalate
crystal associated with a few irregular microbial filaments (see upper
corners of the crystal) with diameters around 0.1
μ
m. The crystal is long
of 2.5
μ
m and has grown in a pit similar to those illustrated in Fig.
5.4b
.
(
f
) Thin filament with
septate
appearance similar to hyphae and
diameters
<
1.0
μ
m likely enveloped by EPS material. Other thicker
filaments (flattened?) appear well-embedded in the pit walls. Sample
MOU19, Mouila old quarry, Gabon (photo mou19-21/2007/ap)
μ
.
Sample MOU26, Mouila old quarry, Gabon (photo mou26-8/2007/ap).
The sample was taken in the domal stromatolite of Fig.
5.3c
before any
previous treatment (acid attack, coloration). (
c
) Small-sized (~30
μ
m)
rounded pit in a dolomicrosparitized mudstone. The pit is filled with
various microbial filaments forming a mesh containing well-
crystallized minerals (see Fig.
5.3e
). The filaments are slightly curved,
some are dichotomous or rod-shaped, and the larger have diameters
varying from 0.5 up to 1
μ
m. The dolomicrospar is irregular, varies in
size between 1 and 3
μ
m and covers partly destroys the filaments.
Thinner and shorter filaments (0.1-0.2
μ
m in diameter) are also present.
'
cavities
'
evaporitic supratidal conditions or subaerial exposition
(MF-MF5) with progressive replacement of primary evapo-
ritic minerals
diagenetically altered upper parts of the cycles are related
to subaqueous deposition of muds associated with desicca-
tion and/or
by
dolomite
(dolomicrosparite). The
intrasediment precipitation of
evaporitic
Search WWH ::

Custom Search