Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Glyceraldehyde-3-P + Pyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate + erythrose-4-P
DAHPS
DXS
1-Deoxy-
D
-arabino-heptulosonate-7-P
1-Deoxy-
D
-xylulose-5-P
DHQS
DXR
3-Dehydroquinate
2-C-Methyl-
D
-erythritol-4-P
DHQ
CMS
3-Dehydroshikimate
-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-
D
-erythritol-4-P
4-(cytidine 5
SDH
ISPE
Shikimate
-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-
D
-erythritol-4-P
2-Phospho-4-(cytidine 5
SK
ISPF
Shikimate-3-P
2-C-Methyl-
D
-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate
EPSPS
HDS
5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-P
1-Hydroxy-2-methyl-2-butenyl-4-diphosphate
CS
HDR
Chorismate
Tryptophan
Isopentenyl-2P
Dimethylallyl-2P
CM
Folate
IPI
Prephenate
GGPS
GPPS
PAT
Arogenate
Phenylalanine
TyrA
PDS
Geranyl-2P
Lycopene
Geranylgeranyl-2P
Tyrosine
LYCB
GGDR
TAT
β
-Carotene
Phytyl-2P
Hydroxyphenylpyruvate
HPPD
Homogentisate
HPT
HST/HGGT
2-Methyl-6-phytylquinol
2-Methyl-6-geranylgeranylbenzoquinol
Phytyl-2P
MPBQMT
MPBQMT
TC
TC
2,3-Dimethyl-6-geranylgeranylbenzoquinol
PK
2,3-Dimethyl-5-phytylquinol
TC
TC
Phytol
-Tocopherol
-Tocopherol
-Tocotrienol
-Tocotrienol
γ
δ
γ
δ
CHL
TMT
TMT
TMT
TMT
Chlorophyll
a
α
-Tocopherol
β
-Tocopherol
α
-Tocotrienol
β
-Tocotrienol
Fig. 8.2.
Biosynthetic routes of vitamin E reactions in plants displaying the methylerythritol 4-phosphate
(MEP), shikimate kinase (SK) and tocopherol core pathways as well as the VTE-related pathways
(carotenoid, chlorophyll, tryptophan, phenylalanine and folate).The corresponding enzymes are: DXS,
deoxy-
D
-xylulose-5- phosphate synthase; DXR, 2-C-methyl-
D
-erythritol 4-phosphate synthase; CMS,
2-C-methyl-
D
-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; ISPE, 4-(cytidine 5
c
-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-
D
-
erythritol kinase; ISPF, 2-C-methyl-
D
-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-
methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase; HDR, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase; IPI,
isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; GPPS, geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; GGPS, geranylgeranyl
pyrophosphate synthase; GGDR, geranylgeranyl reductase; DAHPS, 3-deoxy-
D
-arabino-heptulosonate-7-
phosphate synthase; DHQS, 3-dehydroquinate synthase; SDH, shikimate dehydrogenase; DHQ,
3-dehydroquinate dehydratase; EPSPS, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase; CS, chorismate
synthase; CM, chorismate mutase; PAT, prephenate aminotransferase; TyrA, arogenate dehydrogenase; TAT,
tyrosine aminotransferase; HPPD, 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; HTS/HGGT, homogentisate
solanesyl transferase/homogentisate geranylgeranyl transferase; HPT (VTE2), homogentisate phytyl
transferase; MPBQMT(VTE3), 2-methyl-6-phytyl-1,4-benzoquinone methyltransferase; TC (VTE1),
tocopherol cyclase;
J
-TMT (VTE4),
J
-tocopherol methyl transferase; PK, phytol kinase; CHL, chlorophyllase;
LYCB, lycopene
E
-cyclase. P, phosphate; 2P, diphosphate.
(see Part I). These include the transition
from chloroplasts, which are present in the
green tissues from developing tomato fruit
until the onset of ripening, to carotenoid-
accumulating chromoplasts in the
coloured fruit. Carotenoids present in
chloroplasts are mostly the carotene-
derived xanthophylls, associated with
photosynthesis, whilst in chromoplasts the
acyclic carotenoids (phytoene, phyto-
fl uene,
E
-carotene, neurosporene and
lycopene) accumulate. In tomato, the
transcriptional upregulation of carotenoid
biosynthesis genes is the major regulatory
mechanism that takes place in fruit (Fraser
et al.
, 2009). There is a massive increase in
transcripts for PSY and PDS, concomitant
with a disappearance of the transcripts for
the lycopene cyclases encoded by
LYCB
and
LYCE
. In addition, an alternative set of






















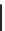





Search WWH ::

Custom Search