Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
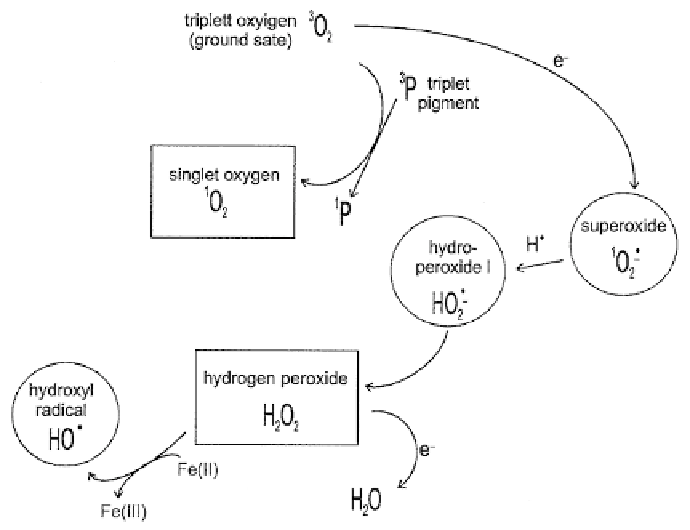
Fig. 2. ROS production from molecular oxygen. Free radical products are encircled, non-radical ROS products
are framed in boxes.
Phenolic compounds may also act as antioxidants. Similarly to ascorbate, they react
with ROS while being converted into a free radical. Radicals formed from antioxidants
are less harmful than ROS and are usually recycled, reduced back to their original
protective form by other antioxidants or enzymes. Their recycling may be delayed when
ROS production is intense, or when enzymes are damaged. In this way, the
accumulation of antioxidant radicals, such as ascorbate [10,11] or phenolic radicals [12]
may serve as a stress marker.
It is important to note that longer life-time (lower reactivity) does not necessary
mean that the ROS is "less damaging'' than an other with shorter life-time (higher
reactivity). Short lived ROS, such as
1
O
2
and
x
OH, react and cause oxidative damage at
the site of their production. Longer lived ones may travel in the membrane and then
react relatively far from their production site where they may initiate reactions yielding
more reactive ROS and thus propagate damage, or may initiate signalling [1].
2.2. DEFENSE
Under physiological conditions ROS production is controlled in plants, these
potentially hazardous chemicals are processed directly at or close to the production site
by the antioxidant systems and thus their concentration is kept low. Enhanced ROS
Search WWH ::

Custom Search