Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Photolyase genes from Norin 1 and from Sasanishiki are currently being cloned
and sequence to determine the exact location(s) of any putative mutations and study
their effect on photolyase function. Since photorepair is the primary DNA repair paths
in plants, these studies should form the basis for determining whether other UV
sensitive cultivars of rice as well as in other species contain mutations in this critical
repair path for UV-induced damage.
8. Polymorphisms of Human Ape1 Gene
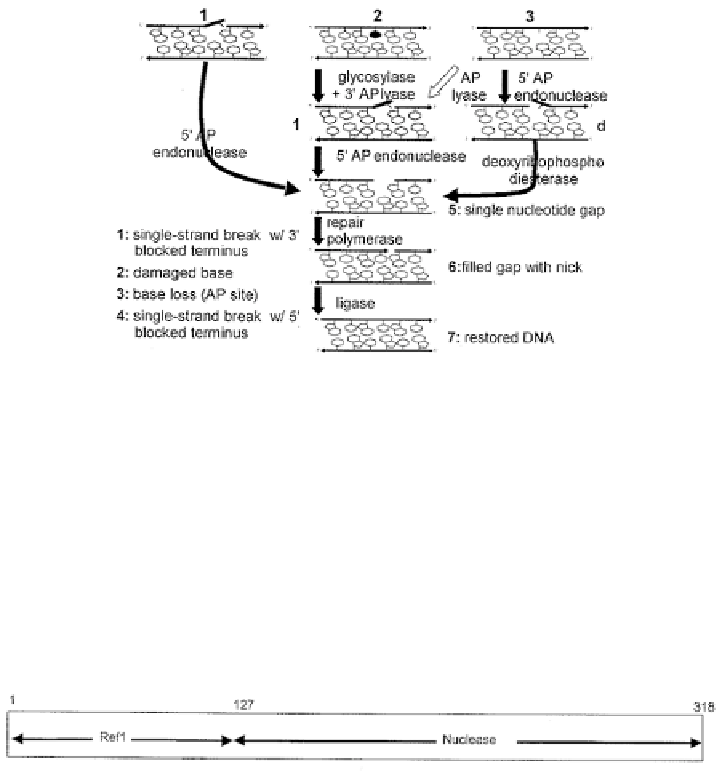
Ape1 is a 5'endonuclease from human cells. It incises DNA at the 5' side of abasic
sites, producing a single strand break with a 3' hydroxyl group and a 5' abasic terminus.
It can also function at radiation-induced single strand breaks, or at sites of base loss
Figure 16. Action of Ape1, a 5´ endonuclease, in DNA repair.
resulting from base excision repair. The resulting nicked DNA is then repaired by a
series of other DNA repair enzymes (See Figure 16). Since abasic sites are produced
by ionizing radiation, by normal metabolism in an oxygen environment, and by
glycosylases during repair of oxidized bases, such an endonuclease is essential for
normal life. Mice that have been genetically engineered to lack Ape1 do not survive
embryogenesis and decreased Ape1 activity has been observed in brain tissue of
patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [6]. The Ape1 gene has been cloned and
sequenced, and the endonuclease has been overproduced, characterized, and its structure
determined by X-ray crystallography. The Ape1 gene has two functional regions, a ref1
domain and a nuclease domain. David Wilson and Harvey Mohrenweiser and their
Figure 17. Human Ape1 Gene with Ref1 and Nuclease Domains.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search