Database Reference
In-Depth Information
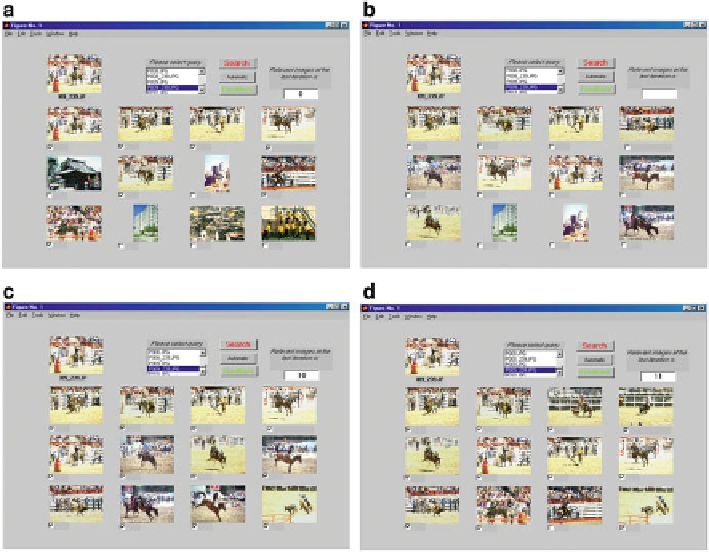
Fig. 3.9
Retrieval results for DB2, obtained by (
a
) a non-adaptive method; (
b
) automatic ARBFN;
(
c
) semiautomatic ARBFN, converted by one round of user interaction; (
d
) user-controlled
ARBFN, converted by two rounds of user interaction
world, the SOTM classifier cannot operate as efficiently as a user-supervised
process. For example, global features of shape, color, or texture might consume an
undue proportion of weights toward the judgment of image relevancy by machine
vision [
75
]. Furthermore, these global features do not always address perceptually
important regions or any salient objects depicted in an image. This is because there
are more regions in an image than those which are of perceptual importance. So,
higher classification accuracy may be possible with the acquisition of more precise
perception information. However, the form of knowledge needed in automatic
relevance feedback has to be identified before the retrieval process begins, instead
of during the process as the user-controlled RF does.
In this section, an automatic adaptive image retrieval scheme is implemented
with embedded knowledge of perceptual importance, the form of which is identified
in advance. With a specific domain to photograph collection, the restricted goal
of identifying the region of interest (ROI) is pursued. The ROI assumes that the
significant objects within an image are often located at the center, as a photographer
usually tries to locate significant objects at the focus of the camera's view. The Edge
Flow model [
94
] is adopted to identify the ROI within a photograph. This ROI does
not necessarily require the exact identification of a possible object in the image, but
Search WWH ::

Custom Search