Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 8.2
Average recall
rate (%), obtained by the
video re-ranking method on
the centralized and the P2P
database systems
Average recall rate (%)
1Iter.
2Iter.
3Iter.
4Iter.
5Iter.
Centralized database
53.31
61.04
61.44
61.44
61.44
P2P database
53.31
62.02
62.99
63.87
64.35
between the non-adaptive retrieval method (1st iteration) and the adaptive retrieval
method (2nd-5th iteration), and not between the centralized and distributed database
systems. It can be observed that the re-ranking process by the adaptive network
significantly improved retrieval performance. The recall rate at the first iteration
was 53.31 % and increased to 62.02 % after one iteration of query modification.
The system converged quickly after two to three iterations. It can be observed
that the retrieval result for the peer-to-peer system was slightly better than that
of the centralized database system. This is because the query modification process
explained in Eq. (
8.22
) allowed each peer node to modify the query (i.e.,
v
q
,
i
,
i
=
1
n
) before computing the final modification of the query at the user node. By
computing
,...,
1
v
q
,
i
in Eq. (
8.22
), the relevant templates were weighted more than
those of the centralized system, in the order of
n
times.
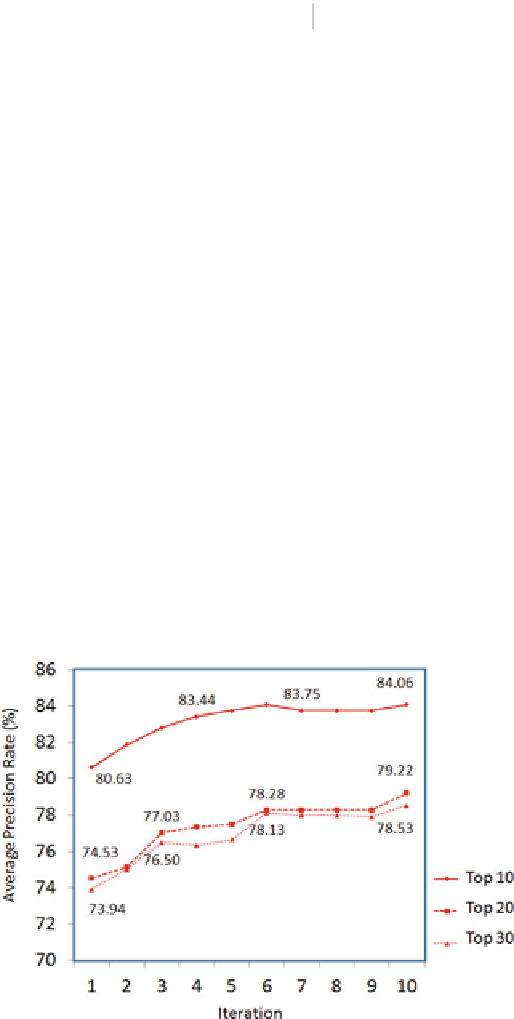
Figure
8.21
shows the average precision rate for the top 10, 20, and 30 retrievals,
obtained by the re-ranking of videos on the P2P network. The precision achieved for
the top ten retrievals was measured to be 80.63 % (more than eight relevant videos
were presented out of the top ten retrieved videos). The precision increased with
the number of iterations of the query modification, and converged to about 84 %
precision.
i
∑
=
Fig. 8.21
Average precision measured for the top 10, 20, and 30 retrievals, obtained by re-ranking
videos in the P2P database

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search