Java Reference
In-Depth Information
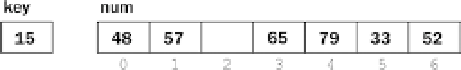
The insertion of
15
in its correct position proceeds as follows:
15
with
79
; it is smaller, so move
79
to location
4
, leaving location
3
free.
This gives the following:
•
Compare
•
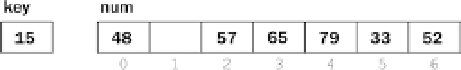
Compare
15
with
65
; it is smaller, so move
65
to location
3
, leaving location
2
free.
This gives the following:
15
with
57
; it is smaller, so move
57
to location
2
, leaving location
1
free.
This gives the following:
•
Compare
•
Compare
15
with
48
; it is smaller, so move
48
to location
1
, leaving location
0
free.
This gives the following:
15
, so it is inserted in location
0
,
•
There are no more numbers to compare with
giving the following:
15
(
key
) by comparing it with the numbers to its left,
starting with the nearest one. As long as
key
is less than
num[k]
, for some
k
, we move
num[k]
to
position
num[k + 1]
and move on to consider
num[k-1]
, providing it exists. It won't exist when
k
is actually
0
. In this case, the process stops, and
key
is inserted in position
0
.
•
We can express the logic of placing
5
th
pass
num[5]
, that is,
33
. This involves placing
33
so that the first six numbers are sorted.
This is done as follows:
•
Process
33
in
key
, leaving location
5
free.
•
Store
33
with
79
; it is smaller, so move
79
to location
5
, leaving location
4
free.
•
Compare
33
with
65
; it is smaller, so move
65
to location
4
, leaving location
3
free.
•
Compare
33
with
57
; it is smaller, so move
57
to location
3
, leaving location
2
free.
•
Compare
33
with
48
; it is smaller, so move
48
to location
2
, leaving location
1
free.
•
Compare



Search WWH ::

Custom Search