Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
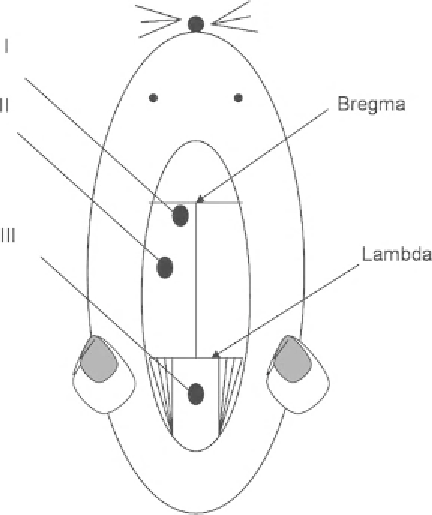
Fig. 1. Schematic presentation of different probe locations in an experimental rat model:
(I) ventricular, (II) intraparenchymal, and (III) cisternal magna cannulation.
3. Stereotactic insertion of a 25-gauge blunt needle into ventricle.
4. Connect via a PE-50 tube with ICP transducer.
5. Further details concerning ventricular cannulation methods
can be found in the manuscript of Hermann et al. (
21
).
1. Drill a small burr hole (diameter: approximately 2 mm) at the
right/left cortex (Fig.
1
):
(a) 1 mm rostral from lambdoid suture; 1.0 mm lateral from
sagittal suture. Or:
(b) 6 mm posterior from bregma; 2.5 mm lateral from midline/
sagittal suture, depth: 2 mm.
2. Incise dura.
3. Zero compensation of the ICP-probe.
4. Implant intraparenchymal ICP-probe, e.g. 4-French fi beroptic
probe (Camino
®
, model 110-4 G, Camino laboratories, San
Diago, USA or: Codman Microsensor Basic Parenchymal
probe, Codman, Germany)
5. ICP-probes can be placed into brain parenchyma (2 mm depth)
with help of a micromanipulator
6. Fixate probe with dental cement to the skull
4.2.2. Intraparenchymal
ICP Measurement
Search WWH ::

Custom Search