Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
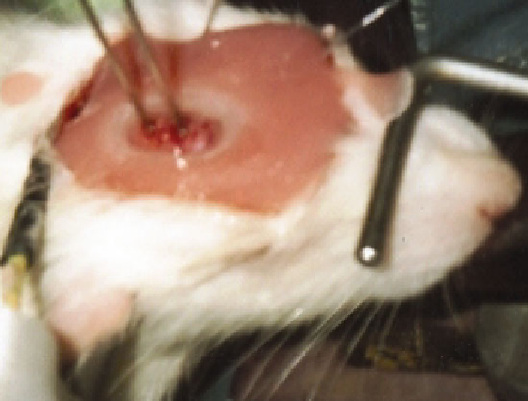
Fig. 3. Open cranial window equipped with two laser-Doppler fl owprobes, a Ag/AgCl wire
electrode to measure the surface DC-ECoG, and an infl ow for the infusion of aCSF into the
window. Ion-selective microelectrodes are not placed yet.
experiment. Avoid placing any glue on the upper side of the coverslip.
Moreover, no glue or cement should enter the artifi cial subdural/
subarachnoid space of the window. If cyanacrylate is used, a layer
of dental cement should be placed around the glue after curing to
secure the window and the tubes. Importantly, always give enough
time for curing (once the window has a leak, it will be very hard to
plug it). Thereafter, the superfusion of aCSF is started and the
outfl ow tube has to be adjusted to an adequate level (3-7 cm
height) to avoid too high or too low hydrostatic pressure (bridge
veins should not be congested between brain and bone rim). If
aCSF drops out of the outfl ow tube, you are done. Then, clean the
coverslip gently, and place and connect the measuring devices.
A resting period of 30-60 min should be included before the
actual measurement is started. It is recommended to test the vas-
cular reactivity after the preparation to ensure preserved vascular
reactivity. For example, this can be performed with a mild hyper-
capnic challenge. The experiment usually starts with recording of
the baseline for another 30-60 min.
4. Cerebral Blood
Flow Measurement
Hemodynamic changes in response to functional activation or SD
have been studied with a variety of methodologies, including laser
Doppler fl owmetry (LDF), laser Doppler perfusion and laser
speckle analysis imaging, direct observation of pial diameter
Search WWH ::

Custom Search